Use of hand hygiene agents as a surrogate marker of compliance in Hungarian long-term care facilities: first nationwide survey
- PMID: 26236475
- PMCID: PMC4521470
- DOI: 10.1186/s13756-015-0069-0
Use of hand hygiene agents as a surrogate marker of compliance in Hungarian long-term care facilities: first nationwide survey
Abstract
Background: Hand hygiene practice is an important measure for preventing infections in long-term care facilities (LTCFs). However, low compliance with hand hygiene has been reported in a number of studies. The purpose of this study was to provide an overview of the first reference data collected on alcohol-based handrub (ABHR) and antiseptic soap consumption, as surrogate markers for hand hygiene compliance by healthcare workers (HCWs) in Hungarian LTCFs. The objective was to inform stakeholders on the need of hand hygiene improvement in these settings.
Methods: Between 5 May and 30 September 2014, we conducted a nationwide, cross-sectional survey using a standardized self-administered questionnaire; all Hungarian LTCFs were eligible. The Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 20.0 was used for data analysis.
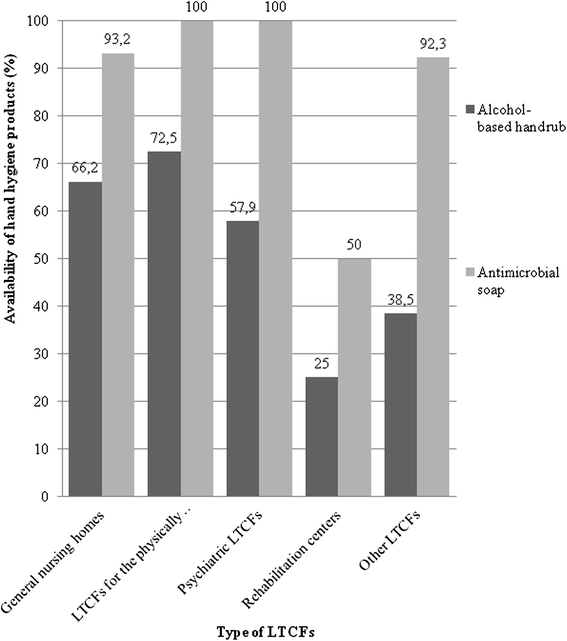
Results: The questionnaire was completed by 354 LTCFs, representing 24 % of all Hungarian LTCFs. In total, the median consumption of ABHR and antimicrobial soap was 15.5 L (IQR, 0-800 L) and 60 L (IQR, 0-1,680 L) per LTCFs, and 2.2 mL (IQR, 0.4-9.1 mL) and 12.1 mL (IQR, 0.7-32.8 mL) per HCWs in 2013, respectively. The estimated number of hand hygiene actions was 0.6 hygienic handrub/HCW per day (IQR, 0-12.8/HCWs) and 2.4 hygienic handwashing/HCW per day (IQR, 0-21.9/HCWs; P = .001), respectively.
Conclusions: This study suggests that non-compliance with hand hygiene is a significant problem in Hungarian LTCFs. Based on our results, there is an urgent need for a nationwide multimodal hand hygiene promotion strategy including education and performance monitoring and feedback in all LTCFs. Furthermore, monitoring of ABHR consumption constitute an additional component of the existing National Nosocomial Surveillance system.
Keywords: Alcohol-based handrub; Compliance; Hand hygiene; Hungary; Long-term care facilities.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of multifaceted hand hygiene interventions in long-term care facilities in Hong Kong: a cluster-randomized controlled trial.Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2012 Aug;33(8):761-7. doi: 10.1086/666740. Epub 2012 Jun 20. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2012. PMID: 22759542 Clinical Trial.
-
Clustered randomized controlled trial of a hand hygiene intervention involving pocket-sized containers of alcohol-based hand rub for the control of infections in long-term care facilities.Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2011 Jan;32(1):67-76. doi: 10.1086/657636. Epub 2010 Nov 18. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2011. PMID: 21087125 Clinical Trial.
-
Hand hygiene practices in a neonatal intensive care unit: a multimodal intervention and impact on nosocomial infection.Pediatrics. 2004 Nov;114(5):e565-71. doi: 10.1542/peds.2004-1107. Epub 2004 Oct 18. Pediatrics. 2004. PMID: 15492360
-
An integrative review of the current evidence on the relationship between hand hygiene interventions and the incidence of health care-associated infections.Am J Infect Control. 2008 Jun;36(5):333-48. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2007.08.007. Am J Infect Control. 2008. PMID: 18538700 Review.
-
Healthcare workers' hand decontamination practices: compliance with recommended guidelines.J Adv Nurs. 2005 Aug;51(3):208-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2005.03490.x. J Adv Nurs. 2005. PMID: 16033588 Review.
Cited by
-
What are the predictors of hand hygiene compliance in the intensive care unit? A cross-sectional observational study.J Infect Prev. 2021 Nov;22(6):252-258. doi: 10.1177/17571774211033351. Epub 2021 Aug 28. J Infect Prev. 2021. PMID: 34880947 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of a 5-year hand hygiene initiative based on the WHO multimodal hand hygiene improvement strategy: an interrupted time-series study.Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2020 May 27;9(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s13756-020-00732-7. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2020. PMID: 32460892 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moro ML, Ricchizzi E, Morsillo F, Marchi M, Puro V, Zotti CM, et al. Infections and antimicrobial resistance in long term care facilities: a national prevalence study. Ann Ig. 2013;25:109–18. - PubMed
-
- Heudorf U, Boehlcke K, Schade M. Healthcare-associated infections in long-term care facilities (HALT) in Frankfurt am Main, Germany, January to March 2011. Euro Surveill. 2012;17:20256. - PubMed
-
- Eilers R, Veldman-Ariesen MJ, Haenen A, van Benthem BH. Prevalence and determinants associated with healthcare-associated infections in long-term care facilities (HALT) in the Netherlands, May to June 2010. Euro Surveill. 2012;17:20252. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources