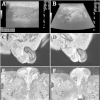
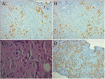
Scrotal wall metastasis from a primary lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 26236609
- PMCID: PMC4501526
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2015.05.002
Scrotal wall metastasis from a primary lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
This a case of a 77 years old male heavy smoker, known to have Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema complicated by a primary invasive adenocarcinoma of the lung with bone metastasis, who presented with a two weeks history of right inguino-scrotal pain and swelling. Imaging studies revealed a right paratesticular formation that appeared to involve the epididymis and the scrotal wall. A biopsy of the mass showed morphological and Immunophenotypic features in favor of metastasis of an adenocarcinoma of the lung. Based on our literature review, there are only few published cases about scrotal wall metastasis of a lung primary.
Keywords: Lung adenocarcinoma; Scrotal metastasis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metastasis of the epididymis and spermatic cord from pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A rare entity. Description of a case and revision of literature.Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2018 Mar 31;90(1):72-73. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2018.1.72. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2018. PMID: 29633804
-
Scrotal wall metastasis as the first manifestation of primary gastric adenocarcinoma.Hong Kong Med J. 2014 Feb;20(1):70-3. doi: 10.12809/hkmj133879. Hong Kong Med J. 2014. PMID: 24473690
-
[A Case of Subcutaneous Scrotal Metastasis from Primary Gastric Cancer].Hinyokika Kiyo. 2020 May;66(5):157-160. doi: 10.14989/ActaUrolJap_66_5_157. Hinyokika Kiyo. 2020. PMID: 32483952 Japanese.
-
Adenocarcinoma of the epididymis: a report of four cases and review of the literature.Am J Surg Pathol. 1997 Dec;21(12):1474-80. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199712000-00010. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997. PMID: 9414191 Review.
-
Metachronous metastasis to inguinal lymph nodes from sigmoid colon adenocarcinoma with abdominal wall metastasis: a case report.BMC Cancer. 2019 Feb 27;19(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5386-x. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30813921 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CCR7 promote lymph node metastasis via regulating VEGF-C/D-R3 pathway in lung adenocarcinoma.J Cancer. 2017 Jul 5;8(11):2060-2068. doi: 10.7150/jca.19069. eCollection 2017. J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28819407 Free PMC article.
-
Size dependent anti-invasiveness of silver nanoparticles in lung cancer cells.RSC Adv. 2019 Jul 5;9(37):21134-21138. doi: 10.1039/c9ra03662h. eCollection 2019 Jul 5. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35521328 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Junyao Li, Ming Yang, Ping Li, Zhenzhong Su, Peng Gao, Jie Zhang. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis will increase the risk of lung cancer. Chin Med J. 2014;127(17):3142–3149. - PubMed
-
- Aubry M.C., Myers J.L., Douglas W.W., Tazelaar H.D., Washington Stephens T.L., Hartman T.E. Primary pulmonary carcinoma in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2002;77:763–770. - PubMed
-
- Usui K., Tanai C., Tanaka Y., Noda H., Ishihara T. The prevalence of pulmonary fibrosis combined with emphysema in patients with lung cancer. Respirology. 2011;16(2):326–331. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources