Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition induces cell cycle arrest and parenchymal damage in renal fibrosis
- PMID: 26236991
- PMCID: PMC4587560
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.3902
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition induces cell cycle arrest and parenchymal damage in renal fibrosis
Abstract
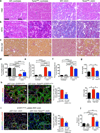
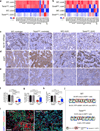
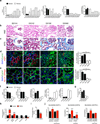
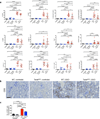
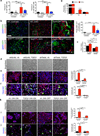
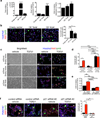
Kidney fibrosis is marked by an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of tubular epithelial cells (TECs). Here we find that, during renal fibrosis, TECs acquire a partial EMT program during which they remain associated with their basement membrane and express markers of both epithelial and mesenchymal cells. The functional consequence of the EMT program during fibrotic injury is an arrest in the G2 phase of the cell cycle and lower expression of several solute and solvent transporters in TECs. We also found that transgenic expression of either Twist1 (encoding twist family bHLH transcription factor 1, known as Twist) or Snai1 (encoding snail family zinc finger 1, known as Snail) expression is sufficient to promote prolonged TGF-β1-induced G2 arrest of TECs, limiting the cells' potential for repair and regeneration. In mouse models of experimentally induced renal fibrosis, conditional deletion of Twist1 or Snai1 in proximal TECs resulted in inhibition of the EMT program and the maintenance of TEC integrity, while also restoring cell proliferation, dedifferentiation-associated repair and regeneration of the kidney parenchyma and attenuating interstitial fibrosis. Thus, inhibition of the EMT program in TECs during chronic renal injury represents a potential anti-fibrosis therapy.
Figures
Comment in
-
A new Twist in kidney fibrosis.Nat Med. 2015 Sep;21(9):975-7. doi: 10.1038/nm.3938. Nat Med. 2015. PMID: 26340117 No abstract available.
-
Epithelial Plasticity versus EMT in Kidney Fibrosis.Trends Mol Med. 2016 Jan;22(1):4-6. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2015.11.009. Epub 2015 Dec 11. Trends Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 26700490 Free PMC article.
References
Online method references
-
- Smyth GK. Limma: linear models for microarray data. In Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions using R and Bioconductor. 2005
-
- Yang J, et al. Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell. 2004;117:927–939. - PubMed
-
- Olive PL, Banath JP. The comet assay: a method to measure DNA damage in individual cells. Nature protocols. 2006;1:23–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

