Unjamming and cell shape in the asthmatic airway epithelium
- PMID: 26237129
- PMCID: PMC4666305
- DOI: 10.1038/nmat4357
Unjamming and cell shape in the asthmatic airway epithelium
Abstract
From coffee beans flowing in a chute to cells remodelling in a living tissue, a wide variety of close-packed collective systems-both inert and living-have the potential to jam. The collective can sometimes flow like a fluid or jam and rigidify like a solid. The unjammed-to-jammed transition remains poorly understood, however, and structural properties characterizing these phases remain unknown. Using primary human bronchial epithelial cells, we show that the jamming transition in asthma is linked to cell shape, thus establishing in that system a structural criterion for cell jamming. Surprisingly, the collapse of critical scaling predicts a counter-intuitive relationship between jamming, cell shape and cell-cell adhesive stresses that is borne out by direct experimental observations. Cell shape thus provides a rigorous structural signature for classification and investigation of bronchial epithelial layer jamming in asthma, and potentially in any process in disease or development in which epithelial dynamics play a prominent role.
Figures

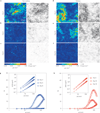

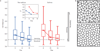
Comment in
-
Tissue mechanics: Cell jam.Nat Mater. 2015 Oct;14(10):970-1. doi: 10.1038/nmat4434. Nat Mater. 2015. PMID: 26395940 No abstract available.
References
-
- Holgate ST. Pathogenesis of asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2008;38:872–897. - PubMed
-
- Friedl P, Gilmour D. Collective cell migration in morphogenesis, regeneration and cancer. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009;10:445–457. - PubMed
-
- Henkes S, Fily Y, Marchetti MC. Active jamming: Self-propelled soft particles at high density. Phys. Rev E. 2011;84:040301. - PubMed
-
- Haeger A, Krause M, Wolf K, Friedl P. Cell jamming: Collective invasion of mesenchymal tumor cells imposed by tissue confinement. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2014;1840:2386–2395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HL007118/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01HL120839/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL107561/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES000002/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- K25 HL111212/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL107561/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL120839/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL102373/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K25 HL091124/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007118/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30ES000002/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- K25HL091124/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL102373/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK065988/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK065988/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

