Randomized placebo-controlled dose-ranging and pharmacodynamics study of roxadustat (FG-4592) to treat anemia in nondialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease (NDD-CKD) patients
- PMID: 26238121
- PMCID: PMC4569392
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfv302
Randomized placebo-controlled dose-ranging and pharmacodynamics study of roxadustat (FG-4592) to treat anemia in nondialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease (NDD-CKD) patients
Abstract
Background: Roxadustat (FG-4592) is an oral hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor that stimulates erythropoiesis. This Phase 2a study tested efficacy (Hb response) and safety of roxadustat in anemic nondialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease (NDD-CKD) subjects.
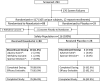
Methods: NDD-CKD subjects with hemoglobin (Hb) ≤11.0 g/dL were sequentially enrolled into four dose cohorts and randomized to roxadustat or placebo two times weekly (BIW) or three times weekly (TIW) for 4 weeks, in an approximate roxadustat:placebo ratio of 3:1. Efficacy was assessed by (i) mean Hb change (ΔHb) from baseline (BL) and (ii) proportion of Hb responders (ΔHb ≥ 1.0 g/dL). Pharmacodynamic evaluation was performed in a subset of subjects. Safety was evaluated by adverse event frequency/severity.
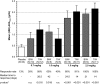
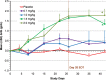
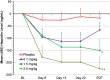
Results: Of 116 subjects receiving treatment, 104 completed 4 weeks of dosing and 96 were evaluable for efficacy. BL characteristics for roxadustat and placebo groups were comparable. In roxadustat-treated subjects, Hb levels increased from BL in a dose-related manner in the 0.7, 1.0, 1.5 and 2.0 mg/kg groups. Maximum ΔHb within the first 6 weeks was significantly higher in the 1.5 and 2.0 mg/kg groups than in the placebo subjects. Hb responder rates were dose dependent and ranged from 30% in the 0.7 mg/kg BIW group to 100% in the 2.0 mg/kg BIW and TIW groups versus 13% in placebo.
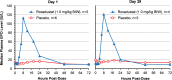
Conclusions: Roxadustat transiently and moderately increased endogenous erythropoietin and reduced hepcidin. Adverse events were similar in the roxadustat and placebo groups. Roxadustat produced dose-dependent increases in blood Hb among anemic NDD-CKD patients in a placebo-controlled trial.
Clinical trials registration: Clintrials.gov #NCT00761657.
Keywords: HIF-PHI; anemia; chronic kidney disease; erythropoietin; hepcidin.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA.
Figures
References
-
- Collins AJ, Ma JZ, Xia A et al. Trends in anemia treatment with erythropoietin usage and patient outcomes. Am J Kidney Dis 1998; 32: S133–S141 - PubMed
-
- Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA 2007; 298: 2038–2047 - PubMed
-
- Eschbach JW, Egrie JC, Downing MR et al. Correction of the anemia of end-stage renal disease with recombinant human erythropoietin. Results of a combined phase I and II clinical trial. N Engl J Med 1987; 316: 73–78 - PubMed
-
- Regidor DL, Kopple JD, Kovesdy CP et al. Associations between changes in hemoglobin and administered erythropoiesis-stimulating agent and survival in hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006; 17: 1181–1191 - PubMed
-
- Revicki DA, Brown RE, Feeny DH et al. Health-related quality of life associated with recombinant human erythropoietin therapy for predialysis chronic renal disease patients. Am J Kidney Dis 1995; 25: 548–554 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

