Species-wide whole genome sequencing reveals historical global spread and recent local persistence in Shigella flexneri
- PMID: 26238191
- PMCID: PMC4522646
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.07335
Species-wide whole genome sequencing reveals historical global spread and recent local persistence in Shigella flexneri
Abstract
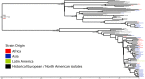
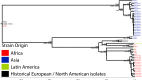
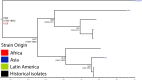
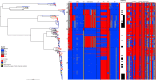
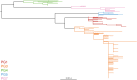
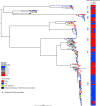
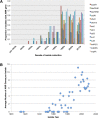
Shigella flexneri is the most common cause of bacterial dysentery in low-income countries. Despite this, S. flexneri remains largely unexplored from a genomic standpoint and is still described using a vocabulary based on serotyping reactions developed over half-a-century ago. Here we combine whole genome sequencing with geographical and temporal data to examine the natural history of the species. Our analysis subdivides S. flexneri into seven phylogenetic groups (PGs); each containing two-or-more serotypes and characterised by distinct virulence gene complement and geographic range. Within the S. flexneri PGs we identify geographically restricted sub-lineages that appear to have persistently colonised regions for many decades to over 100 years. Although we found abundant evidence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) determinant acquisition, our dataset shows no evidence of subsequent intercontinental spread of antimicrobial resistant strains. The pattern of colonisation and AMR gene acquisition suggest that S. flexneri has a distinct life-cycle involving local persistence.
Keywords: E. coli; Shigella; dysentery; epidemiology; genomics; global health; infectious disease; microbiology; pathogen evolution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Al-Hasani K, Henderson IR, Sakellaris H, Rajakumar K, Grant T, Nataro JP, Robins-Browne R, Adler B. The sigA gene which is borne on the she pathogenicity island of Shigella flexneri 2a encodes an exported cytopathic protease involved in intestinal fluid accumulation. Infection and Immunity. 2000;68:2457–2463. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.5.2457-2463.2000. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ashton PM, Baker KS, Gentle A, Wooldridge DJ, Thomson NR, Dallman TJ, Jenkins C. Draft genome sequences of the type strains of Shigella flexneri held at Public Health England: comparison of classical phenotypic and novel molecular assays with whole genome sequence. Gut Pathogens. 2014;6:7. doi: 10.1186/1757-4749-6-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baker KS, Dallman TJ, Ashton PM, Day M, Hughes G, Crook PD, Gilbart VL, Zittermann S, Allen VG, Howden BP, Tomita T, Valcanis M, Harris SR, Connor TR, Sintchenko V, Howard P, Brown JD, Petty NK, Gouali M, Thanh DP, Keddy KH, Smith AM, Talukder KA, Faruque SM, Parkhill J, Baker S, Weill FX, Jenkins C, Thomson NR. Intercontinental dissemination of azithromycin-resistant shigellosis through sexual transmission: a cross-sectional study. The Lancet. Infectious Diseases. 2015 doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(15)00002-X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

