Nonsynaptic junctions on myelinating glia promote preferential myelination of electrically active axons
- PMID: 26238238
- PMCID: PMC4532789
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8844
Nonsynaptic junctions on myelinating glia promote preferential myelination of electrically active axons
Abstract
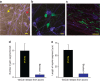
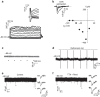
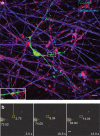
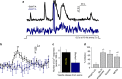
The myelin sheath on vertebrate axons is critical for neural impulse transmission, but whether electrically active axons are preferentially myelinated by glial cells, and if so, whether axo-glial synapses are involved, are long-standing questions of significance to nervous system development, plasticity and disease. Here we show using an in vitro system that oligodendrocytes preferentially myelinate electrically active axons, but synapses from axons onto myelin-forming oligodendroglial cells are not required. Instead, vesicular release at nonsynaptic axo-glial junctions induces myelination. Axons releasing neurotransmitter from vesicles that accumulate in axon varicosities induces a local rise in cytoplasmic calcium in glial cell processes at these nonsynaptic functional junctions, and this signalling stimulates local translation of myelin basic protein to initiate myelination.
Figures
References
-
- Bergles D. E., Roberts J. D., Somogyi P. & Jahr C. E. Glutamatergic synapses on oligodendrocyte precursor cells in the hippocampus. Nature 405, 187–191 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Emery B. Regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation and myelination. Science 330, 779–782 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Fields R. D. Chapter in Neuroglia 3rd edn eds Kettenmann H., Ransom B. R. 573–585Oxford Univ. Press (2013).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

