Trace elements and heavy metals in the Grand Bay National Estuarine Reserve in the northern Gulf of Mexico
- PMID: 26238403
- PMCID: PMC4646843
- DOI: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.07.062
Trace elements and heavy metals in the Grand Bay National Estuarine Reserve in the northern Gulf of Mexico
Abstract
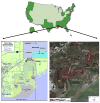
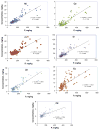
The objectives of this study are to investigate distribution of trace elements and heavy metals in the salt marsh and wetland soil and biogeochemical processes in the Grand Bay National Estuarine Research Reserve of the northern Gulf of Mexico. The results show that Hg, Cd and to some extent, As and Pb have been significantly accumulated in soils. The strongest correlations were found between concentrations of Ni and total organic matter contents. The correlations decreased in the order: Ni>Cr>Sr>Co>Zn, Cd>Cu>Cs. Strong correlations were also observed between total P and concentrations of Ni, Co, Cr, Sr, Zn, Cu, and Cd. This may be related to the P spilling accident in 2005 in the Bangs Lake site. Lead isotopic ratios in soils matched well those of North American coals, indicating the contribution of Pb through atmospheric fallout from coal power plants.
Keywords: Biogeochemical process; Environmental impact; Estuarine chemistry; Grand Bay Reserve; Lead isotopes; Trace elements.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures







References
-
- Adriano D. Trace Elements in Terrestrial Environments: Biogeochemistry, Bioavailability, and Risks of Metals. Springer Verlag; The Netherlands: 2001.
-
- Atkinson NR, Bailey EH, Tye AM, Breward N, Young SD. Fractionation of lead in soil by isotopic dilution and sequential extraction. Environ Chem. 2011;8:493–500.
-
- Aubert H, Pinta M. Trace Elements in Soils. Elsevier; Amsterdam: 1977.
-
- Baur WH, Onishi H. Arsenic. In: Wedepohl KH, editor. Handbook of Geochemistry. 11–3 Springer; Berlin Heidelberg: 1969.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

