Spatiotemporal regulation of Heterochromatin Protein 1-alpha oligomerization and dynamics in live cells
- PMID: 26238434
- PMCID: PMC4523856
- DOI: 10.1038/srep12001
Spatiotemporal regulation of Heterochromatin Protein 1-alpha oligomerization and dynamics in live cells
Abstract
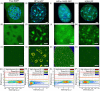
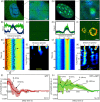
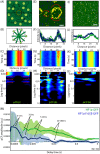
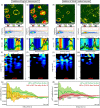
Heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) is a central factor in establishing and maintaining the heterochromatin state. As consequence of playing a structural role in heterochromatin, HP1 proteins can have both an activating as well as repressive function in gene expression. Here we probe how oligomerisation of the HP1-α isoform modulates interaction with chromatin, by spatially resolved fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS). We find from fluctuation analysis of HP1-α dynamics that this isoform exists as a dimer around the periphery of heterochromatin foci and these foci locally rotate with characteristic turn rates that range from 5-100 ms. From inhibition of HP1-α homo-oligomerization we find the slow turn rates (20-100 ms) are dimer dependent. From treatment with drugs that disrupt or promote chromatin compaction, we find that HP1-α dimers spatially redistribute to favor fast (5-10 ms) or slow (20-100 ms) turn rates. Collectively our results demonstrate HP1-α oligomerization is critical to the maintenance of heterochromatin and the tunable dynamics of this HP1 isoform.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High- and low-mobility populations of HP1 in heterochromatin of mammalian cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Jun;15(6):2819-33. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-11-0827. Epub 2004 Apr 2. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15064352 Free PMC article.
-
Differential cooperation between heterochromatin protein HP1 isoforms and MyoD in myoblasts.J Biol Chem. 2008 Aug 29;283(35):23692-700. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802647200. Epub 2008 Jul 2. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18599480 Free PMC article.
-
Maintenance of stable heterochromatin domains by dynamic HP1 binding.Science. 2003 Jan 31;299(5607):721-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1078572. Science. 2003. PMID: 12560555
-
Biochemical and structural properties of heterochromatin protein 1: understanding its role in chromatin assembly.J Biochem. 2014 Jul;156(1):11-20. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvu032. Epub 2014 May 13. J Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24825911 Review.
-
The emerging role of HP1 in the DNA damage response.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Dec;29(24):6335-40. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01048-09. Epub 2009 Oct 5. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19805510 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear bodies formed by polyQ-ataxin-1 protein are liquid RNA/protein droplets with tunable dynamics.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 31;10(1):1557. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-57994-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32005838 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamical organization of the core pluripotency transcription factors responds to differentiation cues in early S-phase.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 May 4;11:1125015. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1125015. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37215075 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying the dynamics of the oligomeric transcription factor STAT3 by pair correlation of molecular brightness.Nat Commun. 2016 Mar 24;7:11047. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11047. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27009358 Free PMC article.
-
Clr4SUV39H1 ubiquitination and non-coding RNA mediate transcriptional silencing of heterochromatin via Swi6 phase separation.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 30;15(1):9384. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53417-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39477922 Free PMC article.
-
Tracking live-cell single-molecule dynamics enables measurements of heterochromatin-associated protein-protein interactions.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Oct 14;52(18):10731-10746. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae692. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39142658 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gorisch S. M., Wachsmuth M., Toth K. F., Lichter P. & Rippe K. Histone acetylation increases chromatin accessibility. J Cell Sci 118, 5825–34 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

