Cerebral amyloid angiopathy and its co-occurrence with Alzheimer's disease and other cerebrovascular neuropathologic changes
- PMID: 26239176
- PMCID: PMC4562901
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.06.028
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy and its co-occurrence with Alzheimer's disease and other cerebrovascular neuropathologic changes
Abstract
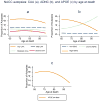
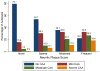
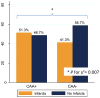
We examined the relationship between cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), Alzheimer's disease neuropathologic changes, other vascular brain pathologies, and cognition in a large multicenter autopsy sample. Data were obtained from the National Alzheimer's Coordinating Center on autopsied subjects (N = 3976) who died between 2002 and 2012. Descriptive statistics and multivariable regression models estimated the associations between CAA and other pathologies, and between CAA severity and cognitive test scores proximal to death. CAA tended to co-occur with Alzheimer's disease neuropathologic changes but a minority of cases were discrepant. CAA was absent in 22% (n = 520) of subjects with frequent neuritic plaques but present in 20.9% (n = 91) of subjects with no neuritic plaques. In subjects with no/sparse neuritic plaques, nonhemorrhagic brain infarcts were more common in those with CAA pathology than without (p = 0.007). In subjects without the APOE ε4 allele, CAA severity was associated with lower cognition proximal to death, factoring in other pathologies. The presence of CAA in patients without Alzheimer's disease may indicate a distinct cerebrovascular condition.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease neuropathologic change; Cerebral amyloid angiopathy; Cerebrovascular disease; Cognition; Neuropathology.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Beekly DL, Ramos EM, van Belle G, Deitrich W, Clark AD, Jacka ME, Kukull WA. The National Alzheimer’s Coordinating Center (NACC) Database: an Alzheimer disease database. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2004;18:270–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 AG013854/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30AG028383/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50AG033514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG023501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005142/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG035982/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008051/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013846/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS061933/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG012300/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016573/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50AG005146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016570/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008017/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS061933/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NR014189/NR/NINR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG025688/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30AG008017/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50AG005131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50AG005142/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG028383/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG033514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

