Electromagnetic radiation at 900 MHz induces sperm apoptosis through bcl-2, bax and caspase-3 signaling pathways in rats
- PMID: 26239320
- PMCID: PMC4523914
- DOI: 10.1186/s12978-015-0062-3
Electromagnetic radiation at 900 MHz induces sperm apoptosis through bcl-2, bax and caspase-3 signaling pathways in rats
Abstract
Background: The decreased reproductive capacity of men is an important factor contributing to infertility. Accumulating evidence has shown that Electromagnetic radiation potentially has negative effects on human health. However, whether radio frequency electromagnetic radiation (RF-EMR) affects the human reproductive system still requires further investigation. Therefore, The present study investigates whether RF-EMR at a frequency of 900 MHz can trigger sperm cell apoptosis and affect semen morphology, concentration, and microstructure.
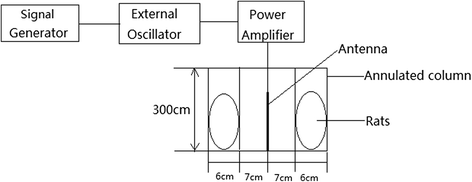
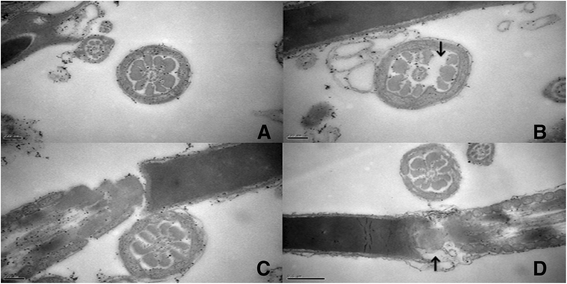
Methods: Twenty four rats were exposed to 900 MHz electromagnetic radiation with a special absorption rate of 0.66 ± 0.01 W/kg for 2 h/d. After 50d, the sperm count, morphology, apoptosis, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and total antioxidant capacity (TAC), representing the sum of enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidants, were investigated. Western blotting and reverse transcriptase PCR were used to determine the expression levels of apoptosis-related proteins and genes, including bcl-2, bax, cytochrome c, and capase-3.
Results: In the present study, the percentage of apoptotic sperm cells in the exposure group was significantly increased by 91.42% compared with the control group. Moreover, the ROS concentration in exposure group was increased by 46.21%, while the TAC was decreased by 28.01%. Radiation also dramatically decreased the protein and mRNA expression of bcl-2 and increased that of bax, cytochrome c, and capase-3.
Conclusion: RF-EMR increases the ROS level and decreases TAC in rat sperm. Excessive oxidative stress alters the expression levels of apoptosis-related genes and triggers sperm apoptosis through bcl-2, bax, cytochrome c and caspase-3 signaling pathways.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

