Continuous Trastuzumab Therapy in Breast Cancer Patients With Asymptomatic Left Ventricular Dysfunction
- PMID: 26240135
- PMCID: PMC4591940
- DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0125
Continuous Trastuzumab Therapy in Breast Cancer Patients With Asymptomatic Left Ventricular Dysfunction
Abstract
Background: Adjuvant trastuzumab is a highly effective targeted treatment that improves survival for patients with HER2-positive breast cancer. However, trastuzumab interruption is recommended for patients who develop treatment-induced cardiotoxicity (i.e., decline in left ventricular ejection fraction [LVEF], with or without symptoms) and can lead to an incomplete course of treatment. We studied the cardiac safety of continuous trastuzumab therapy among patients with asymptomatic declines in LVEF.
Methods: We retrospectively evaluated patients with HER2-positive breast cancer treated with adjuvant trastuzumab at our institution between 2005 and 2010. Treatment-induced cardiotoxicity was defined by an absolute decrease in LVEF of ≥10% to below 55% or an absolute decrease of ≥16%. Logistic regression was used to determine the association between candidate risk factors and treatment-induced cardiotoxicity.
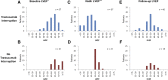
Results: Among 573 patients, 92 (16%) developed treatment-induced cardiotoxicity. Trastuzumab was continued without interruption in 31 of 92 patients with treatment-induced cardiotoxicity—all were asymptomatic with LVEF of ≥50% at cardiotoxicity diagnosis with median LVEF of 53% (range, 50%-63%), and none developed heart failure during follow-up. Risk factors associated with treatment-induced cardiotoxicity included age (p = .011), anthracycline chemotherapy (p = .002), and lower pretrastuzumab LVEF (p < .001).
Conclusion: Among patients who develop asymptomatic treatment-induced cardiotoxicity with LVEF of ≥50%, continuous trastuzumab therapy appears to be safe.
Keywords: Adjuvant chemotherapy; Breast cancer; Cardiotoxicity; Heart failure; Trastuzumab.
©AlphaMed Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures of potential conflicts of interest may be found at the end of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Trastuzumab interruption and treatment-induced cardiotoxicity in early HER2-positive breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015 Jan;149(2):489-95. doi: 10.1007/s10549-014-3253-7. Epub 2015 Jan 1. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015. PMID: 25552363 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of left ventricular diastolic function during trastuzumab treatment in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer.Breast Cancer. 2017 Mar;24(2):312-318. doi: 10.1007/s12282-016-0705-4. Epub 2016 May 27. Breast Cancer. 2017. PMID: 27234030 Clinical Trial.
-
Left ventricular end-diastolic volume as early indicator of trastuzumab-related cardiotoxicity in HER2+ breast cancer patients: results from a single-center retrospective study.Minerva Cardioangiol. 2017 Jun;65(3):278-287. doi: 10.23736/S0026-4725.16.04278-X. Epub 2016 Nov 25. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2017. PMID: 27886160
-
Trastuzumab-related cardiotoxicity: calling into question the concept of reversibility.J Clin Oncol. 2007 Aug 10;25(23):3525-33. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.11.0106. J Clin Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17687157 Review.
-
Cardiotoxicity of novel HER2-targeted therapies.Curr Med Res Opin. 2013 Aug;29(8):1015-24. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2013.807232. Epub 2013 Jun 7. Curr Med Res Opin. 2013. PMID: 23692263 Review.
Cited by
-
Valvular heart disease as a possible predictor of trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity in patients with breast cancer.Mol Clin Oncol. 2019 Jan;10(1):37-42. doi: 10.3892/mco.2018.1764. Epub 2018 Nov 13. Mol Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30655975 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Cardiac Toxicity from Trastuzumab in Patients with Breast Cancer.Curr Breast Cancer Rep. 2017 Sep;9(3):173-182. doi: 10.1007/s12609-017-0249-4. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Curr Breast Cancer Rep. 2017. PMID: 29225726 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiotoxicity Surveillance and Risk of Heart Failure During HER2 Targeted Therapy.JACC CardioOncol. 2020 Jun;2(2):166-175. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2020.03.002. Epub 2020 Jun 16. JACC CardioOncol. 2020. PMID: 33103123 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of obesity, dyslipidemia, and diabetes on trastuzumab-related cardiotoxicity in breast cancer.Curr Oncol. 2019 Jun;26(3):e314-e321. doi: 10.3747/co.26.4823. Epub 2019 Jun 1. Curr Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31285674 Free PMC article.
-
Management of cardiac disease in cancer patients throughout oncological treatment: ESMO consensus recommendations.Ann Oncol. 2020 Feb;31(2):171-190. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2019.10.023. Ann Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31959335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Romond EH, Perez EA, Bryant J, et al. Trastuzumab plus adjuvant chemotherapy for operable HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1673–1684. - PubMed
-
- Piccart-Gebhart MJ, Procter M, Leyland-Jones B, et al. Trastuzumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1659–1672. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

