Quercetin-3-rutinoside Inhibits Protein Disulfide Isomerase by Binding to Its b'x Domain
- PMID: 26240139
- PMCID: PMC4583019
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.666180
Quercetin-3-rutinoside Inhibits Protein Disulfide Isomerase by Binding to Its b'x Domain
Abstract
Quercetin-3-rutinoside inhibits thrombus formation in a mouse model by inhibiting extracellular protein disulfide isomerase (PDI), an enzyme required for platelet thrombus formation and fibrin generation. Prior studies have identified PDI as a potential target for novel antithrombotic agents. Using a fluorescence enhancement-based assay and isothermal calorimetry, we show that quercetin-3-rutinoside directly binds to the b' domain of PDI with a 1:1 stoichiometry. The binding of quercetin-3-rutinoside to PDI induces a more compact conformation and restricts the conformational flexibility of PDI, as revealed by small angle x-ray scattering. The binding sites of quercetin-3-rutinoside to PDI were determined by studying its interaction with isolated fragments of PDI. Quercetin-3-rutinoside binds to the b'x domain of PDI. The infusion of the b'x fragment of PDI rescued thrombus formation that was inhibited by quercetin-3-rutinoside in a mouse thrombosis model. This b'x fragment does not possess reductase activity and, in the absence of quercetin-3-rutinoside, does not affect thrombus formation in vivo. The isolated b' domain of PDI has potential as an antidote to reverse the antithrombotic effect of quercetin-3-rutinoside by binding and neutralizing quercetin-3-rutinoside.
Keywords: PDI; coagulation factor; fibrin; isoquercetin; mouse; platelet; protein-disulfide isomerase; quercetin-3-rutinoside; thrombosis; thrombus formation.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

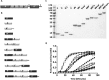
 ; a′, ▵; ab, ♦; bb′, ■; b′xa′, *; abb′, ▴; abb′x, +; bb′xa′, ♢; abb′xa′, ○; abb′xa′c, ●; buffer control, −. Error bars indicate ± S.E. A650, optical density at 650 nm.
; a′, ▵; ab, ♦; bb′, ■; b′xa′, *; abb′, ▴; abb′x, +; bb′xa′, ♢; abb′xa′, ○; abb′xa′c, ●; buffer control, −. Error bars indicate ± S.E. A650, optical density at 650 nm.



References
-
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. (1992) Protein folding in the cell. Nature 355, 33–45 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

