Excess Linoleic Acid Increases Collagen I/III Ratio and "Stiffens" the Heart Muscle Following High Fat Diets
- PMID: 26240151
- PMCID: PMC4645600
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.682195
Excess Linoleic Acid Increases Collagen I/III Ratio and "Stiffens" the Heart Muscle Following High Fat Diets
Abstract
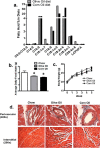
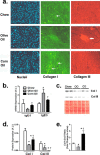
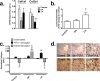
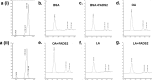
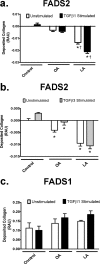
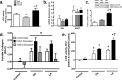
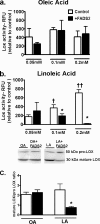
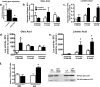
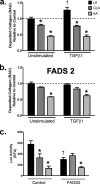
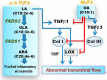
Controversy exists on the benefits versus harms of n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-6 PUFA). Although n-6 PUFA demonstrates anti-atherosclerotic properties, survival following cardiac remodeling may be compromised. We hypothesized that n-6 PUFA like linoleic acid (LA) or other downstream PUFAs like γ-linolenic acid or arachidonic acid alter the transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ)-collagen axis in the heart. Excess dietary LA increased the collagen I/III ratio in the mouse myocardium, leading to cardiac "stiffening" characterized by impaired transmitral flow indicative of early diastolic dysfunction within 5 weeks. In vitro, LA under TGFβ1 stimulation increased collagen I and lysyl oxidase (LOX), the enzyme that cross-links soluble collagen resulting in deposited collagen. Overexpression of fatty acid desaturase 2 (fads2), which metabolizes LA to downstream PUFAs, reduced collagen deposits, LOX maturation, and activity with LA, whereas overexpressing fads1, unrelated to LA desaturation, did not. Furthermore, fads2 knockdown by RNAi elevated LOX activity and collagen deposits in fibroblasts with LA but not oleic acid, implying a buildup of LA for aggravating such pro-fibrotic effects. As direct incubation with γ-linolenic acid or arachidonic acid also attenuated collagen deposits and LOX activity, we concluded that LA itself, independent of other downstream PUFAs, promotes the pro-fibrotic effects of n-6 PUFA. Overall, these results attempt to reconcile opposing views of n-6 PUFA on the cardiovascular system and present evidence supporting a cardiac muscle-specific effect of n-6 PUFAs. Therefore, aggravation of the collagen I/III ratio and cardiac stiffening by excess n-6 PUFA represent a novel pathway of cardiac lipotoxicity caused by high n-6 PUFA diets.
Keywords: collagen; fatty acid metabolism; heart failure; lysyl oxidase; polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA).
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neither linoleic acid nor arachidonic acid promote white adipose tissue inflammation in Fads2-/- mice fed low fat diets.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2017 Nov;126:84-91. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2017.09.008. Epub 2017 Sep 15. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2017. PMID: 29031400
-
Genetic variants in FADS1 and ELOVL2 increase level of arachidonic acid and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in the Tunisian population.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2020 Sep;160:102159. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2020.102159. Epub 2020 Jul 4. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2020. PMID: 32682282
-
Role of lysyl oxidase in myocardial fibrosis: from basic science to clinical aspects.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Jul;299(1):H1-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00335.2010. Epub 2010 May 14. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20472764 Review.
-
Comparative effects of well-balanced diets enriched in α-linolenic or linoleic acids on LC-PUFA metabolism in rat tissues.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2013 May;88(5):383-9. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2013.03.006. Epub 2013 Apr 8. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2013. PMID: 23579035
-
Fatty acids, the immune response, and autoimmunity: a question of n-6 essentiality and the balance between n-6 and n-3.Lipids. 2003 Apr;38(4):323-41. doi: 10.1007/s11745-003-1067-z. Lipids. 2003. PMID: 12848277 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic significance of abnormal matrix collagen remodeling in colorectal cancer based on histologic and bioinformatics analysis.Oncol Rep. 2020 Oct;44(4):1671-1685. doi: 10.3892/or.2020.7729. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Oncol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32945508 Free PMC article.
-
The FADS1 genotypes modify the effect of linoleic acid-enriched diet on adipose tissue inflammation via pro-inflammatory eicosanoid metabolism.Eur J Nutr. 2022 Oct;61(7):3707-3718. doi: 10.1007/s00394-022-02922-y. Epub 2022 Jun 14. Eur J Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35701670 Free PMC article.
-
PUFA Supplementation and Heart Failure: Effects on Fibrosis and Cardiac Remodeling.Nutrients. 2021 Aug 26;13(9):2965. doi: 10.3390/nu13092965. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34578843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-10 improves cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction by stimulating M2 macrophage polarization and fibroblast activation.Basic Res Cardiol. 2017 May;112(3):33. doi: 10.1007/s00395-017-0622-5. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Basic Res Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28439731 Free PMC article.
-
Red blood cell exposure increases chondrocyte susceptibility to oxidative stress following hemarthrosis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2023 Oct;31(10):1365-1376. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2023.06.007. Epub 2023 Jun 25. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2023. PMID: 37364817 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ramsden C. E., Zamora D., Leelarthaepin B., Majchrzak-Hong S. F., Faurot K. R., Suchindran C. M., Ringel A., Davis J. M., Hibbeln J. R. (2013) Use of dietary linoleic acid for secondary prevention of coronary heart disease and death: evaluation of recovered data from the Sydney Diet Heart Study and updated meta-analysis. BMJ 346, e8707. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Harris W. S., Poston W. C., Haddock C. K. (2007) Tissue n-3 and n-6 fatty acids and risk for coronary heart disease events. Atherosclerosis 193, 1–10 - PubMed
-
- Ochoa J. J., Quiles J. L., Huertas J. R., Mataix J. (2005) Coenzyme Q10 protects from aging-related oxidative stress and improves mitochondrial function in heart of rats fed a polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA)-rich diet. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 60, 970–975 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

