Pain from intra-articular NGF or joint injury in the rat requires contributions from peptidergic joint afferents
- PMID: 26240991
- PMCID: PMC4568150
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.07.043
Pain from intra-articular NGF or joint injury in the rat requires contributions from peptidergic joint afferents
Abstract
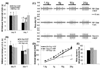
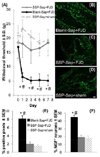
Non-physiological stretch of the cervical facet joint's capsular ligament induces persistent behavioral hypersensitivity and spinal neuronal hyperexcitability via an intra-articular NGF-dependent mechanism. Although that ligament is innervated by nociceptors, it is unknown if a subpopulation is exclusively responsible for the behavioral and spinal neuronal responses to intra-articular NGF and/or facet joint injury. This study ablated joint afferents using the neurotoxin saporin targeted to neurons involved in either peptidergic ([Sar(9),Met (O2)(11)]-substance P-saporin (SSP-Sap)) or non-peptidergic (isolectin B4-saporin (IB4-Sap)) signaling to investigate the contributions of those neuronal populations to facet-mediated pain. SSP-Sap, but not IB4-Sap, injected into the bilateral C6/C7 facet joints 14 days prior to an intra- articular NGF injection prevents NGF-induced mechanical and thermal hypersensitivity in the forepaws. Similarly, only SSP- Sap prevents the increase in mechanical forepaw stimulation- induced firing of spinal neurons after intra-articular NGF. In addition, intra-articular SSP-Sap prevents both behavioral hypersensitivity and upregulation of NGF in the dorsal root ganglion after a facet joint distraction that normally induces pain. These findings collectively suggest that disruption of peptidergic signaling within the joint may be a potential treatment for facet pain, as well as other painful joint conditions associated with elevated NGF, such as osteoarthritis.
Keywords: Afferent; Facet joint; NGF; Neuronal hyperexcitability; Pain; Trauma.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors contributed substantially to the manuscript and approved the final content. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Johannes CB, Le TK, Zhou X, Johnston JA, Dworkin RH. The prevalence of chronic pain in United States adults: results of an internet-based survey. J. Pain. 2010;11:1230–1239. - PubMed
-
- Lord SM, Barnsley L, Wallis BJ, McDonald GJ, Bogduk N. Percutaneous radio-frequency neurotomy for chronic cervical zygapophyseal-joint pain. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996;335:1721–1726. - PubMed
-
- Pearson AM, Ivancic PC, Ito S, Panjabi MM. Facet joint kinematics and injury mechanisms during simulated whiplash. Spine. 2004;29:390–397. - PubMed
-
- Lu Y, Chen C, Kallakuri S, Patwardhan A, Cavanaugh JM. Neurophysiological and biomechanical characterization of goat cervical facet joint capsules. J. Orthop. Res. 2005;23:779–787. - PubMed
-
- Cavanaugh JM, el-Bohy A, Hardy WN, Getchell TV, Getchell ML, King AI. Sensory innervation of soft tissues of the lumbar spine in the rat. J. Orthop. Res. 1989;7:378–388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

