The Right Tool for the Job: Detection of Soil-Transmitted Helminths in Areas Co-endemic for Other Helminths
- PMID: 26241329
- PMCID: PMC4524677
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003967
The Right Tool for the Job: Detection of Soil-Transmitted Helminths in Areas Co-endemic for Other Helminths
Abstract
Background: Due to the recent increased use of the McMaster (MM) fecal egg counting method for assessing benzimidazole drug efficacy for treating soil-transmitted helminth (STH) infections, the aim of the current study was to determine the operational value of including the MM method alongside the Kato-Katz (KK) fecal thick smear to increase the diagnostic sensitivity when STHs are co-endemic with trematode helminths (e.g., Schistosoma mansoni).
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted in school-aged children aged 4-18 years in the northeastern region of the State of Minas Gerais (Brazil), where Necator americanus, Ascaris lumbricoides, Trichuris trichiura, and S. mansoni are co-endemic. One fecal sample from each participant was collected and transported to the field laboratory for analysis. Coprological diagnosis was performed on each fecal sample by three different methods: Formalin-Ether Sedimentation (FES), KK and the MM technique. The diagnostic sensitivity and negative predictive value (NPV) of each technique was calculated using the combination of all three techniques as the composite standard. In order to determine the agreement between the three techniques Fleiss´ kappa was used. Both the Cure Rate (CR) and the Fecal Egg Count Reduction (FECR) were calculated using the two quantification techniques (i.e., the MM and KK).
Results: Fecal samples from 1260 children were analyzed. The KK had higher diagnostic sensitivity than the MM for the detection of both A. lumbricoides (KK 97.3%, MM 69.5%) and hookworm (KK 95.1%, MM 80.8%). The CR of a single dose of mebendazole varied significantly between the KK and MM for both A. lumbricoides (p = 0.016) and hookworm (p = 0.000), with lower rates obtained with the KK. On the other hand, the FECR was very similar between both techniques for both A. lumbricoides and hookworm.
Conclusion: The MM did not add any diagnostic value over the KK in areas where both STHs and trematodes were co-endemic. The lower sensitivity of the MM would have an important impact on the administration of selective school-based treatment in this area since if only the MM were used, 36 (13.9%) children diagnosed with A. lumbricoides would have gone untreated.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
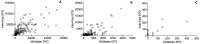
Similar articles
-
Comparison of three copromicroscopic methods to assess albendazole efficacy against soil-transmitted helminth infections in school-aged children on Pemba Island.Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2013 Aug;107(8):493-501. doi: 10.1093/trstmh/trt051. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2013. PMID: 23843559 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of the Kato-Katz and FLOTAC techniques for the diagnosis of soil-transmitted helminth infections.Parasitol Int. 2011 Dec;60(4):398-402. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2011.06.020. Epub 2011 Jun 25. Parasitol Int. 2011. PMID: 21726662
-
Comparison of individual and pooled stool samples for the assessment of intensity of Schistosoma mansoni and soil-transmitted helminth infections using the Kato-Katz technique.Parasit Vectors. 2015 Sep 24;8:489. doi: 10.1186/s13071-015-1101-1. Parasit Vectors. 2015. PMID: 26400064 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of single-dose 500 mg mebendazole in soil-transmitted helminth infections: a review.J Helminthol. 2018 May;92(3):269-278. doi: 10.1017/S0022149X17000426. Epub 2017 Jul 18. J Helminthol. 2018. PMID: 28716158 Review.
-
Soil-transmitted helminths and schistosome infections in Ethiopia: a systematic review of progress in their control over the past 20 years.Parasit Vectors. 2021 Feb 5;14(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-04600-0. Parasit Vectors. 2021. PMID: 33546757 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Kato-Katz and Lumbreras rapid sedimentation test to evaluate helminth prevalence in the setting of a school-based deworming program.Pathog Glob Health. 2016 May;110(3):130-4. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2016.1187361. Pathog Glob Health. 2016. PMID: 27376503 Free PMC article.
-
Advantages and Limitations of Microscopy and Molecular Detections for Diagnosis of Soil-transmitted Helminths: An Overview.Helminthologia. 2022 Dec 30;59(4):321-340. doi: 10.2478/helm-2022-0034. eCollection 2022 Dec. Helminthologia. 2022. PMID: 36875683 Free PMC article.
-
Urgent needs in fostering neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) laboratory capacity in WHO Western Pacific Region: results from the external quality assessment on NTDs diagnosis in 2012-2015.Infect Dis Poverty. 2017 Jun 8;6(1):106. doi: 10.1186/s40249-017-0319-x. Infect Dis Poverty. 2017. PMID: 28592266 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Techniques for Soil-Transmitted Helminths - Recent Advances.Res Rep Trop Med. 2021 Aug 4;12:181-196. doi: 10.2147/RRTM.S278140. eCollection 2021. Res Rep Trop Med. 2021. PMID: 34377048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing stool quantities generated by three specific Kato-Katz thick smear templates employed in different settings.Infect Dis Poverty. 2016 Jul 1;5(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s40249-016-0150-9. Infect Dis Poverty. 2016. PMID: 27364623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mejia R, Vicuna Y, Broncano N, Sandoval C, Vaca M, et al. (2013) A novel, multi-parallel, real-time polymerase chain reaction approach for eight gastrointestinal parasites provides improved diagnostic capabilities to resource-limited at-risk populations. Am J Trop Med Hyg 88: 1041–1047. 10.4269/ajtmh.12-0726 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ministry of Agriculture Fisheries and Food (1977) Manual of Veterinary Parasitological Laboratory Techniques. London, UK: Her Majesty’s Stationary Office (HMSO).
-
- Katz N, Chaves A, Pellegrino J (1972) A simple device for quantitative stool thick-smear technique in Schistosomiasis mansoni. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 14: 397–400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

