"PP2C7s", Genes Most Highly Elaborated in Photosynthetic Organisms, Reveal the Bacterial Origin and Stepwise Evolution of PPM/PP2C Protein Phosphatases
- PMID: 26241330
- PMCID: PMC4524716
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132863
"PP2C7s", Genes Most Highly Elaborated in Photosynthetic Organisms, Reveal the Bacterial Origin and Stepwise Evolution of PPM/PP2C Protein Phosphatases
Abstract
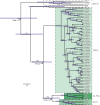
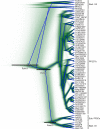
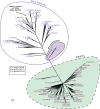
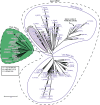
Mg+2/Mn+2-dependent type 2C protein phosphatases (PP2Cs) are ubiquitous in eukaryotes, mediating diverse cellular signaling processes through metal ion catalyzed dephosphorylation of target proteins. We have identified a distinct PP2C sequence class ("PP2C7s") which is nearly universally distributed in Eukaryotes, and therefore apparently ancient. PP2C7s are by far most prominent and diverse in plants and green algae. Combining phylogenetic analysis, subcellular localization predictions, and a distillation of publically available gene expression data, we have traced the evolutionary trajectory of this gene family in photosynthetic eukaryotes, demonstrating two major sequence assemblages featuring a succession of increasingly derived sub-clades. These display predominant expression moving from an ancestral pattern in photosynthetic tissues toward non-photosynthetic, specialized and reproductive structures. Gene co-expression network composition strongly suggests a shifting pattern of PP2C7 gene functions, including possible regulation of starch metabolism for one homologue set in Arabidopsis and rice. Distinct plant PP2C7 sub-clades demonstrate novel amino terminal protein sequences upon motif analysis, consistent with a shifting pattern of regulation of protein function. More broadly, neither the major events in PP2C sequence evolution, nor the origin of the diversity of metal binding characteristics currently observed in different PP2C lineages, are clearly understood. Identification of the PP2C7 sequence clade has allowed us to provide a better understanding of both of these issues. Phylogenetic analysis and sequence comparisons using Hidden Markov Models strongly suggest that PP2Cs originated in Bacteria (Group II PP2C sequences), entered Eukaryotes through the ancestral mitochondrial endosymbiosis, elaborated in Eukaryotes, then re-entered Bacteria through an inter-domain gene transfer, ultimately producing bacterial Group I PP2C sequences. A key evolutionary event, occurring first in ancient Eukaryotes, was the acquisition of a conserved aspartate in classic Motif 5. This has been inherited subsequently by PP2C7s, eukaryotic PP2Cs and bacterial Group I PP2Cs, where it is crucial to the formation of a third metal binding pocket, and catalysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evolution of bacterial-like phosphoprotein phosphatases in photosynthetic eukaryotes features ancestral mitochondrial or archaeal origin and possible lateral gene transfer.Plant Physiol. 2013 Dec;163(4):1829-43. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.224378. Epub 2013 Oct 9. Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24108212 Free PMC article.
-
Type 2C protein phosphatases in plants.FEBS J. 2013 Jan;280(2):681-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08670.x. Epub 2012 Jul 17. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 22726910 Review.
-
Evolutionary radiation pattern of novel protein phosphatases revealed by analysis of protein data from the completely sequenced genomes of humans, green algae, and higher plants.Plant Physiol. 2008 Feb;146(2):351-67. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.111393. Epub 2007 Dec 21. Plant Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18156295 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and evolutionary analyses of the PP2C gene family with their expression profiling in response to multiple stresses in Brachypodium distachyon.BMC Genomics. 2016 Mar 3;17:175. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2526-4. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26935448 Free PMC article.
-
Protein phosphatase 2C (PP2C) function in higher plants.Plant Mol Biol. 1998 Dec;38(6):919-27. doi: 10.1023/a:1006054607850. Plant Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9869399 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of nutrients on the function of the chlamydial Rsb partner switching mechanism.Pathog Dis. 2022 Nov 29;80(1):ftac044. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftac044. Pathog Dis. 2022. PMID: 36385643 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of chloroplast-localized protein phosphatase 2Cs in Arabidopsis thaliana leads to enhancement of plant immunity and resistance to Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris infection.Mol Plant Pathol. 2018 May;19(5):1184-1195. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12596. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Mol Plant Pathol. 2018. PMID: 28815858 Free PMC article.
-
Pptc7 is an essential phosphatase for promoting mammalian mitochondrial metabolism and biogenesis.Nat Commun. 2019 Jul 19;10(1):3197. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11047-6. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31324765 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Kinases and Phosphatases of the Plastid and Their Potential Role in Starch Metabolism.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Jul 17;9:1032. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01032. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30065742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Origin of the Phosphoprotein Phosphatase (PPP) sequence family in Bacteria: Critical ancestral sequence changes, radiation patterns and substrate binding features.BBA Adv. 2021 Feb 18;1:100005. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadva.2021.100005. eCollection 2021. BBA Adv. 2021. PMID: 37082010 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

