Spatially-global integration of closed, fragmented contours by finding the shortest-path in a log-polar representation
- PMID: 26241462
- PMCID: PMC4752937
- DOI: 10.1016/j.visres.2015.06.007
Spatially-global integration of closed, fragmented contours by finding the shortest-path in a log-polar representation
Abstract
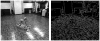
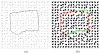
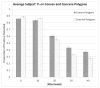
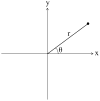
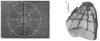
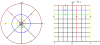
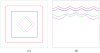
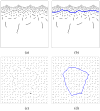
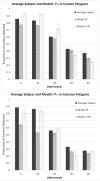
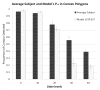
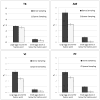
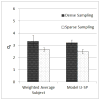
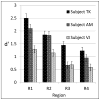
Finding the occluding contours of objects in real 2D retinal images of natural 3D scenes is done by determining, which contour fragments are relevant, and the order in which they should be connected. We developed a model that finds the closed contour represented in the image by solving a shortest path problem that uses a log-polar representation of the image; the kind of representation known to exist in area V1 of the primate cortex. The shortest path in a log-polar representation favors the smooth, convex and closed contours in the retinal image that have the smallest number of gaps. This approach is practical because finding a globally-optimal solution to a shortest path problem is computationally easy. Our model was tested in four psychophysical experiments. In the first two experiments, the subject was presented with a fragmented convex or concave polygon target among a large number of unrelated pieces of contour (distracters). The density of these pieces of contour was uniform all over the screen to minimize spatially-local cues. The orientation of each target contour fragment was randomly perturbed by varying the levels of jitter. Subjects drew a closed contour that represented the target's contour on a screen. The subjects' performance was nearly perfect when the jitter-level was low. Their performance deteriorated as jitter-levels were increased. The performance of our model was very similar to our subjects'. In two subsequent experiments, the subject was asked to discriminate a briefly-presented egg-shaped object while maintaining fixation at several different positions relative to the closed contour of the shape. The subject's discrimination performance was affected by the fixation position in much the same way as the model's.
Keywords: Closed contour; Figure Ground Organization; Log-polar representation; Shortest path.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
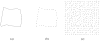












Similar articles
-
A shape-level flanker facilitation effect in contour integration and the role of shape complexity.Vision Res. 2019 May;158:221-236. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2019.02.002. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Vision Res. 2019. PMID: 30797765
-
Contour integration with corners.Vision Res. 2016 Oct;127:132-140. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2016.07.010. Epub 2016 Aug 31. Vision Res. 2016. PMID: 27542687
-
The role of crowding in contextual influences on contour integration.J Vis. 2012 Jul 9;12(7):3. doi: 10.1167/12.7.3. J Vis. 2012. PMID: 22776847
-
Perception of contours and shapes: low and intermediate stage mechanisms.Vision Res. 2008 Sep;48(20):2106-27. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2008.03.006. Epub 2008 May 27. Vision Res. 2008. PMID: 18502467 Review.
-
Neural basis of shape representation in the primate brain.Prog Brain Res. 2006;154:293-313. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(06)54016-6. Prog Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 17010719 Review.
Cited by
-
Seeing our 3D world while only viewing contour-drawings.PLoS One. 2021 Jan 22;16(1):e0242581. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242581. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33481778 Free PMC article.
-
Combining contour and region for closed boundary extraction of a shape.Front Psychol. 2023 Nov 15;14:1198691. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1198691. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 38034308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anstis SM. A chart demonstrating variations in acuity with retinal position. Vision Research. 1974;14(7):589–592. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Shahar O, Ben-Yosef G. Tangent bundle elastica and computer vision. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 2015;37:161–174. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Yosef G, Ben-Shahar O. A tangent bundle theory for visual curve completion. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 2012;34:1263–1280. - PubMed
-
- Bertamini M. The importance of being convex: An advantage for convexity when judging position. Perception. 2001;30(11):1295–1310. - PubMed
-
- Bertamini M, Wagemans J. Processing convexity and concavity along a 2-D contour: figure-ground, structural shape, and attention. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review. 2013;20(2):191–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

