Identification of MicroRNAs in Meloidogyne incognita Using Deep Sequencing
- PMID: 26241472
- PMCID: PMC4524723
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133491
Identification of MicroRNAs in Meloidogyne incognita Using Deep Sequencing
Abstract
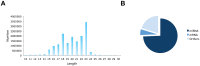
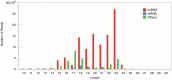
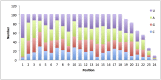
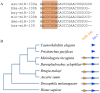
MicroRNAs play important regulatory roles in eukaryotic lineages. In this paper, we employed deep sequencing technology to sequence and identify microRNAs in M. incognita genome, which is one of the important plant parasitic nematodes. We identified 102 M. incognita microRNA genes, which can be grouped into 71 nonredundant miRNAs based on mature sequences. Among the 71 miRANs, 27 are known miRNAs and 44 are novel miRNAs. We identified seven miRNA clusters in M. incognita genome. Four of the seven clusters, miR-100/let-7, miR-71-1/miR-2a-1, miR-71-2/miR-2a-2 and miR-279/miR-2b are conserved in other species. We validated the expressions of 5 M. incognita microRNAs, including 3 known microRNAs (miR-71, miR-100b and let-7) and 2 novel microRNAs (NOVEL-1 and NOVEL-2), using RT-PCR. We can detect all 5 microRNAs. The expression levels of four microRNAs obtained using RT-PCR were consistent with those obtained by high-throughput sequencing except for those of let-7. We also examined how M. incognita miRNAs are conserved in four other nematodes species: C. elegans, A. suum, B. malayi and P. pacificus. We found that four microRNAs, miR-100, miR-92, miR-279 and miR-137, exist only in genomes of parasitic nematodes, but do not exist in the genomes of the free living nematode C. elegans. Our research created a unique resource for the research of plant parasitic nematodes. The candidate microRNAs could help elucidate the genomic structure, gene regulation, evolutionary processes, and developmental features of plant parasitic nematodes and nematode-plant interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Stage-Wise Identification and Analysis of miRNA from Root-Knot Nematode Meloidogyne incognita.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Oct 21;17(10):1758. doi: 10.3390/ijms17101758. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27775666 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of microRNAs in the plant parasitic root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita using deep sequencing.Funct Integr Genomics. 2016 Mar;16(2):127-42. doi: 10.1007/s10142-015-0472-x. Epub 2016 Jan 7. Funct Integr Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26743520
-
Small RNA Sequencing Reveals Regulatory Roles of MicroRNAs in the Development of Meloidogyne incognita.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 2;20(21):5466. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215466. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31684025 Free PMC article.
-
Application of small RNA technology for improved control of parasitic helminths.Vet Parasitol. 2015 Aug 15;212(1-2):47-53. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2015.06.003. Epub 2015 Jun 9. Vet Parasitol. 2015. PMID: 26095949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
tRFs: miRNAs in disguise.Gene. 2016 Apr 1;579(2):133-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.12.058. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Gene. 2016. PMID: 26743126 Review.
Cited by
-
Stage-Wise Identification and Analysis of miRNA from Root-Knot Nematode Meloidogyne incognita.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Oct 21;17(10):1758. doi: 10.3390/ijms17101758. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27775666 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analysis and miRNA Target Profiling at Various Stages of Root-Knot Nematode Meloidogyne incognita Development for Identification of Potential Regulatory Networks.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 12;22(14):7442. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147442. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299062 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicle-Contained microRNA of C. elegans as a Tool to Decipher the Molecular Basis of Nematode Parasitism.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 May 25;10:217. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00217. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32523895 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the putative microRNAs cross-kingdom transfer in Solanum lycopersicum-Meloidogyne incognita interactions.Front Plant Sci. 2024 May 8;15:1383986. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1383986. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38784062 Free PMC article.
-
Small RNA Sequencing Based Identification of MiRNAs in Daphnia magna.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 14;10(9):e0137617. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137617. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26367422 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281–97. Epub 2004/01/28. doi: S0092867404000455 [pii]. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

