CD163 interacts with TWEAK to regulate tissue regeneration after ischaemic injury
- PMID: 26242746
- PMCID: PMC4918310
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8792
CD163 interacts with TWEAK to regulate tissue regeneration after ischaemic injury
Abstract
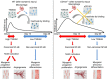
Macrophages are an essential component of the immune response to ischaemic injury and play an important role in promoting inflammation and its resolution, which is necessary for tissue repair. The type I transmembrane glycoprotein CD163 is exclusively expressed on macrophages, where it acts as a receptor for haemoglobin:haptoglobin complexes. An extracellular portion of CD163 circulates in the blood as a soluble protein, for which no physiological function has so far been described. Here we show that during ischaemia, soluble CD163 functions as a decoy receptor for TWEAK, a secreted pro-inflammatory cytokine of the tumour necrosis factor family, to regulate TWEAK-induced activation of canonical nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and Notch signalling necessary for myogenic progenitor cell proliferation. Mice with deletion of CD163 have transiently elevated levels of TWEAK, which stimulate muscle satellite cell proliferation and tissue regeneration in their ischaemic and non-ischaemic limbs. These results reveal a role for soluble CD163 in regulating muscle regeneration after ischaemic injury.
Figures
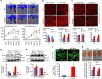
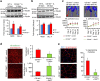
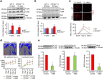
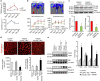
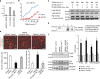
 P<0.05 versus other groups in d,e. Comparisons between groups were achieved using a two-sided student's t-test. For multiple group comparisons, we utilized a one-way ANOVA. If the variance ratio test (F-test) was significant, a more detailed post hoc analysis of differences between groups was made using a Tukey–Kramer honest significance difference test.
P<0.05 versus other groups in d,e. Comparisons between groups were achieved using a two-sided student's t-test. For multiple group comparisons, we utilized a one-way ANOVA. If the variance ratio test (F-test) was significant, a more detailed post hoc analysis of differences between groups was made using a Tukey–Kramer honest significance difference test.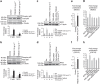
References
-
- Lloyd-Jones D. et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2009 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation 119, 480–486 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Gordon S. Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3, 23–35 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Kristiansen M. et al. Identification of the haemoglobin scavenger receptor. Nature 409, 198–201 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

