Effects of aluminum on the reduction of neural stem cells, proliferating cells, and differentiating neuroblasts in the dentate gyrus of D-galactose-treated mice via increasing oxidative stress
- PMID: 26243606
- PMCID: PMC4921660
- DOI: 10.4142/jvs.2016.17.2.127
Effects of aluminum on the reduction of neural stem cells, proliferating cells, and differentiating neuroblasts in the dentate gyrus of D-galactose-treated mice via increasing oxidative stress
Abstract
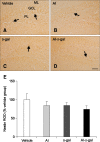
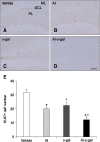
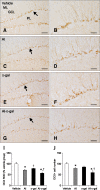
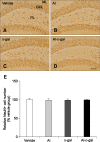
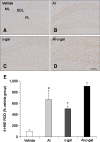
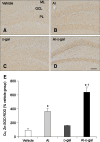
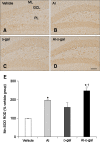
Aluminum (Al) accumulation increases with aging, and long-term exposure to Al is regarded as a risk factor for Alzheimer's disease. In this study, we investigated the effects of Al and/or D-galactose on neural stem cells, proliferating cells, differentiating neuroblasts, and mature neurons in the hippocampal dentate gyrus. AlCl3 (40 mg/kg/day) was intraperitoneally administered to C57BL/6J mice for 4 weeks. In addition, vehicle (physiological saline) or D-galactose (100 mg/kg) was subcutaneously injected to these mice immediately after AlCl3 treatment. Neural stem cells, proliferating cells, differentiating neuroblasts, and mature neurons were detected using the relevant marker for each cell type, including nestin, Ki67, doublecortin, and NeuN, respectively, via immunohistochemistry. Subchronic (4 weeks) exposure to Al in mice reduced neural stem cells, proliferating cells, and differentiating neuroblasts without causing any changes to mature neurons. This Al-induced reduction effect was exacerbated in D-galactose-treated mice compared to vehicle-treated adult mice. Moreover, exposure to Al enhanced lipid peroxidation in the hippocampus and expression of antioxidants such as Cu, Zn- and Mn-superoxide dismutase in D-galactose-treated mice. These results suggest that Al accelerates the reduction of neural stem cells, proliferating cells, and differentiating neuroblasts in D-galactose-treated mice via oxidative stress, without inducing loss in mature neurons.
Keywords: D-galactose; adult neurogenesis; aluminum; hippocampus; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Melatonin improves D-galactose-induced aging effects on behavior, neurogenesis, and lipid peroxidation in the mouse dentate gyrus via increasing pCREB expression.J Pineal Res. 2012 Jan;52(1):21-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00912.x. Epub 2011 Jul 1. J Pineal Res. 2012. PMID: 21718363
-
Valeriana officinalis extract and its main component, valerenic acid, ameliorate D-galactose-induced reductions in memory, cell proliferation, and neuroblast differentiation by reducing corticosterone levels and lipid peroxidation.Exp Gerontol. 2013 Nov;48(11):1369-77. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2013.09.002. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Exp Gerontol. 2013. PMID: 24055511
-
Additive or synergistic effects of aluminum on the reduction of neural stem cells, cell proliferation, and neuroblast differentiation in the dentate gyrus of high-fat diet-fed mice.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2014 Jan;157(1):51-9. doi: 10.1007/s12011-013-9861-y. Epub 2013 Nov 22. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2014. PMID: 24265032
-
Melatonin ameliorates cuprizone-induced reduction of hippocampal neurogenesis, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and phosphorylation of cyclic AMP response element-binding protein in the mouse dentate gyrus.Brain Behav. 2019 Sep;9(9):e01388. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1388. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Brain Behav. 2019. PMID: 31429533 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of antipsychotics on dentate gyrus stem cell proliferation and survival in animal models: a critical update.Neural Plast. 2012;2012:832757. doi: 10.1155/2012/832757. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Neural Plast. 2012. PMID: 23150836 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Aluminium Contamination on the Nervous System of Freshwater Aquatic Vertebrates: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 21;23(1):31. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010031. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008450 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdel Moneim AE, Othman MS, Mohmoud SM, El-Deib KM. Pomegranate peel attenuates aluminum-induced hepatorenal toxicity. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2013;23:624–633. - PubMed
-
- Ball MJ, Fisman M, Hachinski V, Blume W, Fox A, Kral VA, Kirshen AJ, Fox H, Merskey H. A new definition of Alzheimer's disease: a hippocampal dementia. Lancet. 1985;1:14–16. - PubMed
-
- Bignucolo A, Lemire J, Auger C, Castonguay Z, Appanna V, Appanna VD. The molecular connection between aluminum toxicity, anemia, inflammation and obesity: therapeutic cues. In: Silverberg D, editor. Anemia. Rijeka: InTech; 2012. pp. 403–424.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

