SHORT VEGETATIVE PHASE Up-Regulates TEMPRANILLO2 Floral Repressor at Low Ambient Temperatures
- PMID: 26243615
- PMCID: PMC4587448
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.15.00570
SHORT VEGETATIVE PHASE Up-Regulates TEMPRANILLO2 Floral Repressor at Low Ambient Temperatures
Abstract
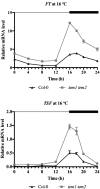
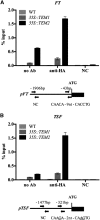
Plants integrate day length and ambient temperature to determine the optimal timing for developmental transitions. In Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), the floral integrator FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) and its closest homolog TWIN SISTER OF FT promote flowering in response to their activator CONSTANS under long-day inductive conditions. Low ambient temperature (16°C) delays flowering, even under inductive photoperiods, through repression of FT, revealing the importance of floral repressors acting at low temperatures. Previously, we have reported that the floral repressors TEMPRANILLO (TEM; TEM1 and TEM2) control flowering time through direct regulation of FT at 22°C. Here, we show that tem mutants are less sensitive than the wild type to changes in ambient growth temperature, indicating that TEM genes may play a role in floral repression at 16°C. Moreover, we have found that TEM2 directly represses the expression of FT and TWIN SISTER OF FT at 16°C. In addition, the floral repressor SHORT VEGETATIVE PHASE (SVP) directly regulates TEM2 but not TEM1 expression at 16°C. Flowering time analyses of svp tem mutants indicate that TEM may act in the same genetic pathway as SVP to repress flowering at 22°C but that SVP and TEM are partially independent at 16°C. Thus, TEM2 partially mediates the temperature-dependent function of SVP at low temperatures. Taken together, our results indicate that TEM genes are also able to repress flowering at low ambient temperatures under inductive long-day conditions.
© 2015 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Andrés F, Coupland G (2012) The genetic basis of flowering responses to seasonal cues. Nat Rev Genet 13: 627–639 - PubMed
-
- Bergonzi S, Albani MC (2011) Reproductive competence from an annual and a perennial perspective. J Exp Bot 62: 4415–4422 - PubMed
-
- Blázquez MA, Ahn JH, Weigel D (2003) A thermosensory pathway controlling flowering time in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Genet 33: 168–171 - PubMed
-
- Capovilla G, Schmid M, Posé D (2015) Control of flowering by ambient temperature. J Exp Bot 66: 59–69 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

