Noninvasive cerebral oximetry during endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke: an observational study
- PMID: 26243709
- PMCID: PMC4635248
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2015.181
Noninvasive cerebral oximetry during endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke: an observational study
Abstract
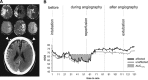
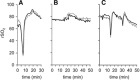
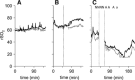
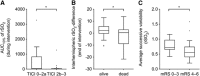
Implementing endovascular stroke care often impedes neurologic assessment in patients who need sedation or general anesthesia. Cerebral near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) may help physicians monitor cerebral tissue viability, but data in hyperacute stroke patients receiving endovascular treatment are sparse. In this observational study, the NIRS index regional oxygen saturation (rSO2) was measured noninvasively before, during, and after endovascular therapy via bilateral forehead NIRS optodes. During the study period, 63 patients were monitored with NIRS; 43 qualified for analysis. Before recanalization, 10 distinct rSO2 decreases occurred in 11 patients with respect to time to intubation. During recanalization, two kinds of unilateral rSO2 changes occurred in the affected hemisphere: small peaks throughout the treatment (n=14, 32.6%) and sustained increases immediately after recanalization (n=2, 4.7%). Lower area under the curve 10% below baseline was associated with better reperfusion status (thrombolysis in cerebral infarction ≥ 2b, P=0.009). At the end of the intervention, lower interhemispheric rSO2 difference predicted death within 90 days (P=0.037). After the intervention, higher rSO2 variability predicted poor outcome (modified Rankin scale > 3, P=0.032). Our findings suggest that bi-channel rSO2-NIRS has potential for guiding neuroanesthesia and predicting outcome. To better monitor local revascularization, an improved stroke-specific set-up in future studies is necessary.
Conflict of interest statement
Christian Hametner received congress fee support from the company (Covidien) that manufactures the near-infrared spectroscopy device used in this study.
Roland Veltkamp received consulting honoraria from Covidien.
Julian Bösel received travel support and speaker honoraria from Covidien.
Covidien had no influence whatsoever on the design, the conduct, the data selection, or the data analysis in this study. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Limit of intraoperative near-infrared spectroscopy monitoring during endovascular thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke.Interv Neuroradiol. 2018 Feb;24(1):57-63. doi: 10.1177/1591019917740101. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Interv Neuroradiol. 2018. PMID: 29183174 Free PMC article.
-
A noninvasive estimation of mixed venous oxygen saturation using near-infrared spectroscopy by cerebral oximetry in pediatric cardiac surgery patients.Paediatr Anaesth. 2005 Jun;15(6):495-503. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9592.2005.01488.x. Paediatr Anaesth. 2005. PMID: 15910351
-
Usefulness of near-infrared spectroscopy in thrombectomy monitoring.J Clin Monit Comput. 2015 Oct;29(5):585-9. doi: 10.1007/s10877-014-9636-9. Epub 2014 Nov 4. J Clin Monit Comput. 2015. PMID: 25367227
-
Is bridging with intravenous thrombolysis of any benefit in endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke?World Neurosurg. 2014 Sep-Oct;82(3-4):e453-8. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2013.01.097. Epub 2013 Feb 1. World Neurosurg. 2014. PMID: 23376392 Review.
-
Intraoperative monitoring of cerebral oximetry and depth of anaesthesia during neuroanesthesia procedures.Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2016 Oct;29(5):576-81. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0000000000000371. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2016. PMID: 27367415 Review.
Cited by
-
No-reflow after recanalization in ischemic stroke: From pathomechanisms to therapeutic strategies.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2024 Jun;44(6):857-880. doi: 10.1177/0271678X241237159. Epub 2024 Feb 29. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2024. PMID: 38420850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Propagating Relationship of Cerebral Oximetric Volume and the Clinical Outcome of Recombinant Tissue Plasminogen Activator (r-TPA) Therapy on Acute Cerebral Ischemic Stroke Patients.Adv J Emerg Med. 2019 Aug 17;4(1):e7. doi: 10.22114/ajem.v0i0.174. eCollection 2020 Winter. Adv J Emerg Med. 2019. PMID: 31938776 Free PMC article.
-
Real-Time Non-invasive Assessment of Cerebral Hemodynamics With Diffuse Optical Spectroscopies in a Neuro Intensive Care Unit: An Observational Case Study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2020 Apr 28;7:147. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00147. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32411712 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of general anesthesia on serum β-amyloid protein and regional cerebral oxygen saturation of elderly patients after subtotal gastrectomy.Exp Ther Med. 2016 Dec;12(6):3561-3566. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3814. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Exp Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 28101151 Free PMC article.
-
High-normal PaCO2 values might be associated with worse outcome in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage - a retrospective cohort study.BMC Neurol. 2020 Jan 20;20(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s12883-020-1603-0. BMC Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31959120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 1Berkhemer OA, Fransen PS, Beumer D, van den Berg LA, Lingsma HF, Yoo AJ et al. A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 2015; 372: 11–20. - PubMed
-
- 2Campbell BC, Mitchell PJ, Kleinig TJ, Dewey HM, Churilov L, Yassi N et al. Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N Engl J Med 2015; 372: 1009–1018. - PubMed
-
- 3Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, Eesa M, Rempel JL, Thornton J et al. Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 2015; 372: 1019–1030. - PubMed
-
- 5Froehler MT, Fifi JT, Majid A, Bhatt A, Ouyang M, McDonagh DL. Anesthesia for endovascular treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Neurology 2012; 79: S167–S173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

