Efficacy and Tolerability of Generic Mirtazapine (Mirtax) for Major Depressive Disorder: Multicenter, Open-label, Uncontrolled, Prospective Study
- PMID: 26243840
- PMCID: PMC4540031
- DOI: 10.9758/cpn.2015.13.2.144
Efficacy and Tolerability of Generic Mirtazapine (Mirtax) for Major Depressive Disorder: Multicenter, Open-label, Uncontrolled, Prospective Study
Abstract
Objective: Mirtax is a generic mirtazapine widely used since 2003. We conducted an open-label, uncontrolled 6-week study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Mirtax for major depressive disorder (MDD).
Methods: Ninety three MDD patients with the diagnosis of MDD and 17-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS) score ≥14 were recruited. The HDRS, Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS), and the Clinical Global Impressions-Severity Scale (CGI-S) were administered at baseline, 1, 2, 4 and 6 weeks. Response (≥50% decrease in the HDRS or MADRS score), remission (absolute HDRS score ≤7 or MADRS score ≤10) and CGI-I score ≤2 were also calculated. Adverse event (AE) frequency and severity, weight, blood pressure, and pulse rate were checked to assess safety.
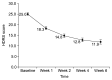
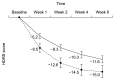
Results: The starting dosage was 11.5±6.4 mg/day, and the maintenance dosage was 23.1±9.4 mg/day. During 6 weeks, HDRS, MADRS and CGI-S scores decreased from 25.1±5.6 to 11.9±8.6 (mean change -13.1±8.3, p<0.001), from 30.2±6.3 to 13.73±10.40 (mean change -16.5±9.8, p<0.001), and from 5.0±0.8 to 2.5±1.3 (mean change -2.5±1.3, p<0.001), respectively. The percentages of responders, remitters by HDRS and patients with a CGI-I score ≤2 were 64.6%, 35.4% and 52.7%, respectively. Significant decreases in HDRS, MADRS and CGI-S scores were confirmed at week 1. The total rate of AEs was 32.3%; the most frequently reported AEs were sedation (4.3%) and constipation (4.3%). Weight was increased from 58.8±10.6 to 60.3±9.3 kg (mean change 0.7±1.7 kg, p=0.004).
Conclusion: This study, as the first clinical trial of generic mirtazapine, demonstrated the efficacy and tolerability of Mirtax for MDD using a single treatment design.
Keywords: Efficacy; Generic drugs; Mirtazapine; Tolerability.
Figures

References
-
- Thompson C. Mirtazapine versus selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. J Clin Psychiatry. 1999;60( Suppl 17):18–22. discussion 46–48. - PubMed
-
- Benkert O, Szegedi A, Philipp M, Kohnen R, Heinrich C, Heukels A, et al. Mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets versus venlafaxine extended release: a double-blind, randomized multicenter trial comparing the onset of antidepressant response in patients with major depressive disorder. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2006;26:75–78. doi: 10.1097/01.jcp.0000194622.99986.d6. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

