A Non-enveloped Virus Hijacks Host Disaggregation Machinery to Translocate across the Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane
- PMID: 26244546
- PMCID: PMC4526233
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005086
A Non-enveloped Virus Hijacks Host Disaggregation Machinery to Translocate across the Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane
Abstract
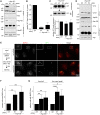
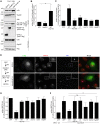
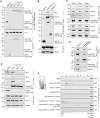
Mammalian cytosolic Hsp110 family, in concert with the Hsc70:J-protein complex, functions as a disaggregation machinery to rectify protein misfolding problems. Here we uncover a novel role of this machinery in driving membrane translocation during viral entry. The non-enveloped virus SV40 penetrates the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane to reach the cytosol, a critical infection step. Combining biochemical, cell-based, and imaging approaches, we find that the Hsp110 family member Hsp105 associates with the ER membrane J-protein B14. Here Hsp105 cooperates with Hsc70 and extracts the membrane-penetrating SV40 into the cytosol, potentially by disassembling the membrane-embedded virus. Hence the energy provided by the Hsc70-dependent Hsp105 disaggregation machinery can be harnessed to catalyze a membrane translocation event.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
SGTA-Dependent Regulation of Hsc70 Promotes Cytosol Entry of Simian Virus 40 from the Endoplasmic Reticulum.J Virol. 2017 May 26;91(12):e00232-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00232-17. Print 2017 Jun 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28356524 Free PMC article.
-
Bag2 Is a Component of a Cytosolic Extraction Machinery That Promotes Membrane Penetration of a Nonenveloped Virus.J Virol. 2018 Jul 17;92(15):e00607-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00607-18. Print 2018 Aug 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29769335 Free PMC article.
-
The endoplasmic reticulum membrane J protein C18 executes a distinct role in promoting simian virus 40 membrane penetration.J Virol. 2015 Apr;89(8):4058-68. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03574-14. Epub 2015 Jan 28. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25631089 Free PMC article.
-
SV40 Hijacks Cellular Transport, Membrane Penetration, and Disassembly Machineries to Promote Infection.Viruses. 2019 Oct 5;11(10):917. doi: 10.3390/v11100917. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31590347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A bacterial toxin and a nonenveloped virus hijack ER-to-cytosol membrane translocation pathways to cause disease.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2015;50(6):477-88. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2015.1085826. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26362261 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Components of the LINC and NPC complexes coordinately target and translocate a virus into the nucleus to promote infection.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Sep 6;18(9):e1010824. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010824. eCollection 2022 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 36067270 Free PMC article.
-
The atlastin ER morphogenic proteins promote formation of a membrane penetration site during non-enveloped virus entry.J Virol. 2023 Aug 31;97(8):e0075623. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00756-23. Epub 2023 Aug 14. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37578227 Free PMC article.
-
ER functions are exploited by viruses to support distinct stages of their life cycle.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Oct 30;48(5):2173-2184. doi: 10.1042/BST20200395. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 33119046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A plant reovirus hijacks the DNAJB12-Hsc70 chaperone complex to promote viral spread in its planthopper vector.Mol Plant Pathol. 2022 Jun;23(6):805-818. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13152. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Mol Plant Pathol. 2022. PMID: 34668642 Free PMC article.
-
Golgi-associated BICD adaptors couple ER membrane penetration and disassembly of a viral cargo.J Cell Biol. 2020 May 4;219(5):e201908099. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201908099. J Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32259203 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

