Hippocampal Synaptic Expansion Induced by Spatial Experience in Rats Correlates with Improved Information Processing in the Hippocampus
- PMID: 26244549
- PMCID: PMC4526663
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132676
Hippocampal Synaptic Expansion Induced by Spatial Experience in Rats Correlates with Improved Information Processing in the Hippocampus
Erratum in
-
Correction: Hippocampal Synaptic Expansion Induced by Spatial Experience in Rats Correlates with Improved Information Processing in the Hippocampus.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 8;10(9):e0137944. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137944. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26349078 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
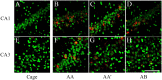
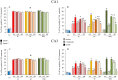
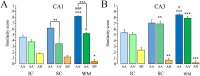
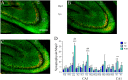
Spatial water maze (WM) overtraining induces hippocampal mossy fiber (MF) expansion, and it has been suggested that spatial pattern separation depends on the MF pathway. We hypothesized that WM experience inducing MF expansion in rats would improve spatial pattern separation in the hippocampal network. We first tested this by using the the delayed non-matching to place task (DNMP), in animals that had been previously trained on the water maze (WM) and found that these animals, as well as animals treated as swim controls (SC), performed better than home cage control animals the DNMP task. The "catFISH" imaging method provided neurophysiological evidence that hippocampal pattern separation improved in animals treated as SC, and this improvement was even clearer in animals that experienced the WM training. Moreover, these behavioral treatments also enhance network reliability and improve partial pattern separation in CA1 and pattern completion in CA3. By measuring the area occupied by synaptophysin staining in both the stratum oriens and the stratun lucidum of the distal CA3, we found evidence of structural synaptic plasticity that likely includes MF expansion. Finally, the measures of hippocampal network coding obtained with catFISH correlate significantly with the increased density of synaptophysin staining, strongly suggesting that structural synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus induced by the WM and SC experience is related to the improvement of spatial information processing in the hippocampus.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Spatial memory training induces morphological changes detected by manganese-enhanced MRI in the hippocampal CA3 mossy fiber terminal zone.Neuroimage. 2016 Mar;128:227-237. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.07.084. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Neuroimage. 2016. PMID: 26254115
-
Synaptogenesis of mossy fibers induced by spatial water maze overtraining.Hippocampus. 1999;9(6):631-6. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1063(1999)9:6<631::AID-HIPO3>3.0.CO;2-3. Hippocampus. 1999. PMID: 10641755
-
Spatial long-term memory is related to mossy fiber synaptogenesis.J Neurosci. 2001 Sep 15;21(18):7340-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-18-07340.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11549744 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal synaptic plasticity: role in spatial learning or the automatic recording of attended experience?Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1997 Oct 29;352(1360):1489-503. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1997.0136. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1997. PMID: 9368938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen-mediated structural and functional synaptic plasticity in the female rat hippocampus.Horm Behav. 1998 Oct;34(2):140-8. doi: 10.1006/hbeh.1998.1466. Horm Behav. 1998. PMID: 9799624 Review.
Cited by
-
3,5-T2 and 3,3',5-T3 Regulate Cerebellar Thyroid Hormone Signalling and Myelin Molecular Dynamics in Tilapia.Sci Rep. 2019 May 14;9(1):7359. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43701-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31089165 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloidosis is associated with thicker myelin and increased oligodendrogenesis in the adult mouse brain.J Neurosci Res. 2020 Oct;98(10):1905-1932. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24672. Epub 2020 Jun 18. J Neurosci Res. 2020. PMID: 32557778 Free PMC article.
-
Trace eyeblink conditioning is associated with changes in synaptophysin immunoreactivity in the cerebellar interpositus nucleus in guinea pigs.Biosci Rep. 2018 May 8;38(3):BSR20170335. doi: 10.1042/BSR20170335. Print 2018 Jun 29. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29051391 Free PMC article.
-
Correction: Hippocampal Synaptic Expansion Induced by Spatial Experience in Rats Correlates with Improved Information Processing in the Hippocampus.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 8;10(9):e0137944. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137944. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26349078 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Locus Coeruleus Phasic, But Not Tonic, Activation Initiates Global Remapping in a Familiar Environment.J Neurosci. 2019 Jan 16;39(3):445-455. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1956-18.2018. Epub 2018 Nov 26. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30478033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ramírez-Amaya V, Escobar ML, Chao V, Bermúdez-Rattoni F. Synaptogenesis of mossy fibers induced by spatial water maze overtraining. Hippocampus. 1999; 9: 631–6. - PubMed
-
- Holahan MR, Rekart JL, Sandoval J, Routtenberg A. Spatial learning induces presynaptic structural remodeling in the hippocampal mossy fiber system of two rat strains. Hippocampus. 2006;16: 560–70. - PubMed
-
- Middei S, Vetere G, Sgobio C, Ammassari-Teule M. Landmark-based but not vestibular-based orientation elicits mossy fiber synaptogenesis in the mouse hippocampus. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2007; 87: 174–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

