Near Work Related Parameters and Myopia in Chinese Children: the Anyang Childhood Eye Study
- PMID: 26244865
- PMCID: PMC4526691
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134514
Near Work Related Parameters and Myopia in Chinese Children: the Anyang Childhood Eye Study
Abstract
Purpose: To examine the associations of near work related parameters with spherical equivalent refraction and axial length in Chinese children.
Methods: A total of 1770 grade 7 students with mean age of 12.7 years were examined with cycloplegic autorefraction and axial length. Questions were asked regarding time spent in near work and outdoors per day, and near work related parameters.
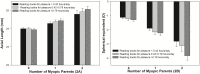
Results: Multivariate models revealed the following associations with greater odds of myopia: continuous reading (> 45min), odds ratio [OR], 1.4; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.1-1.8; close television viewing distance (≤ 3m), OR, 1.7; 95% CI, 1.2-2.3; head tilt when writing, OR, 1.3; 95% CI, 1.1-1.7, and desk lighting using fluorescent vs. incandescent lamp, OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.2-2.0. These factors, together with close reading distance and close nib-to-fingertip distance were significantly associated with greater myopia (P<0.01). Among near work activities, only reading more books for pleasure was significantly associated with greater myopia (P=0.03). Television viewing distance (≤ 3 m), fluorescent desk light, close reading distance (≤20 cm) and close nib-to-fingertip distance (≤ 2 cm) were significantly associated with longer axial length (P<0.01). Reading distance, desk light, and reading books for pleasure had significant interaction effects with parental myopia.
Conclusions: Continuous reading, close distances of reading, television viewing and nib-to-fingertip, head tilt when writing, reading more books for pleasure and use of fluorescent desk light were significantly associated with myopia in 12-year-old Chinese children, which indicates that visual behaviors and environments may be important factors mediating the effects of near work on myopia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

