Clade-Specific Quantitative Analysis of Photosynthetic Gene Expression in Prochlorococcus
- PMID: 26244890
- PMCID: PMC4526520
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133207
Clade-Specific Quantitative Analysis of Photosynthetic Gene Expression in Prochlorococcus
Abstract
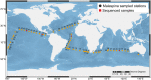
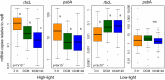
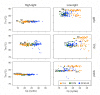
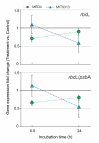
Newly designed primers targeting rbcL (CO2 fixation), psbA (photosystem II) and rnpB (reference) genes were used in qRT-PCR assays to assess the photosynthetic capability of natural communities of Prochlorococcus, the most abundant photosynthetic organism on Earth and a major contributor to primary production in oligotrophic oceans. After optimizing sample collection methodology, we analyzed a total of 62 stations from the Malaspina 2010 circumnavigation (including Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans) at three different depths. Sequence and quantitative analyses of the corresponding amplicons showed the presence of high-light (HL) and low-light (LL) Prochlorococcus clades in essentially all 182 samples, with a largely uniform stratification of LL and HL sequences. Synechococcus cross-amplifications were detected by the taxon-specific melting temperatures of the amplicons. Laboratory exposure of Prochlorococcus MED4 (HL) and MIT9313 (LL) strains to organic pollutants (PAHs and organochlorine compounds) showed a decrease of rbcL transcript abundances, and of the rbcL to psbA ratios for both strains. We propose this technique as a convenient assay to evaluate effects of environmental stressors, including pollution, on the oceanic Prochlorococcus photosynthetic function.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dysregulation of photosynthetic genes in oceanic Prochlorococcus populations exposed to organic pollutants.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 14;7(1):8029. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08425-9. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28808349 Free PMC article.
-
Widespread metabolic potential for nitrite and nitrate assimilation among Prochlorococcus ecotypes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jun 30;106(26):10787-92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0902532106. Epub 2009 Jun 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19549842 Free PMC article.
-
Potential photosynthesis gene recombination between Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus via viral intermediates.Environ Microbiol. 2005 Oct;7(10):1505-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00833.x. Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16156724
-
A minimum set of regulators to thrive in the ocean.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2020 Mar 1;44(2):232-252. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuaa005. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32077939 Review.
-
Cyanobacterial photosynthesis in the oceans: the origins and significance of divergent light-harvesting strategies.Trends Microbiol. 2002 Mar;10(3):134-42. doi: 10.1016/s0966-842x(02)02319-3. Trends Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11864823 Review.
Cited by
-
Dysregulation of photosynthetic genes in oceanic Prochlorococcus populations exposed to organic pollutants.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 14;7(1):8029. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08425-9. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28808349 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial consumption of organophosphate esters in seawater under phosphorus limited conditions.Sci Rep. 2019 Jan 18;9(1):233. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36635-2. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30659251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li WK. Composition of ultraphytoplankton in the central north Atlantic. Marine Ecology Progress Series. 1995;122(1–3):1–8.
-
- Veldhuis MJW, Kraay GW, Van Bleijswijk JDL, Baars MA. Seasonal and spatial variability in phytoplankton biomass, productivity and growth in the northwestern Indian ocean: The southwest and northeast monsoon, 1992–1993. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers. 1997;44(3):425–49.
-
- Goericke R, Welschmeyer NA. The marine prochlorophyte Prochlorococcus contributes significantly to phytoplankton biomass and primary production in the Sargasso Sea. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers. 1993;40(11 /12):2283–94.
-
- Liu H, Nolla HA, Campbell L. Prochlorococcus growth rate and contribution to primary production in the equatorial and subtropical North Pacific Ocean. Aquatic Microbial Ecology. 1997;12(1):39–47.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

