Identification and Characterization of MicroRNAs from Longitudinal Muscle and Respiratory Tree in Sea Cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) Using High-Throughput Sequencing
- PMID: 26244987
- PMCID: PMC4526669
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134899
Identification and Characterization of MicroRNAs from Longitudinal Muscle and Respiratory Tree in Sea Cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) Using High-Throughput Sequencing
Abstract
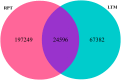
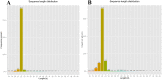
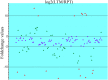
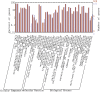
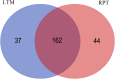
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), as a family of non-coding small RNAs, play important roles in the post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. Sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) is an important economic species which is widely cultured in East Asia. The longitudinal muscle (LTM) and respiratory tree (RPT) are two important tissues in sea cucumber, playing important roles such as respiration and movement. In this study, we identified and characterized miRNAs in the LTM and RPT of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) using Illumina HiSeq 2000 platform. A total of 314 and 221 conserved miRNAs were identified in LTM and RPT, respectively. In addition, 27 and 34 novel miRNAs were identified in the LTM and RPT, respectively. A set of 58 miRNAs were identified to be differentially expressed between LTM and RPT. Among them, 9 miRNAs (miR-31a-3p, miR-738, miR-1692, let-7a, miR-72a, miR-100b-5p, miR-31b-5p, miR-429-3p, and miR-2008) in RPT and 7 miRNAs (miR-127, miR-340, miR-381, miR-3543, miR-434-5p, miR-136-3p, and miR-300-3p) in LTM were differentially expressed with foldchange value being greater than 10. A total of 14,207 and 12,174 target genes of these miRNAs were predicted, respectively. Functional analysis of these target genes of miRNAs were performed by GO analysis and pathway analysis. This result provided in this work will be useful for understanding biological characteristics of the LTM and RPT of sea cucumber and assisting molecular breeding of sea cucumber for aquaculture.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expression analysis of microRNAs related to the skin ulceration syndrome of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016 Feb;49:205-12. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2015.12.036. Epub 2015 Dec 24. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26723265
-
Large-scale identification and comparative analysis of miRNA expression profile in the respiratory tree of the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus during aestivation.Mar Genomics. 2014 Feb;13:39-44. doi: 10.1016/j.margen.2014.01.002. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Mar Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24444870
-
Understanding regulation of microRNAs on intestine regeneration in the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus using high-throughput sequencing.Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics. 2017 Jun;22:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cbd.2017.01.001. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28160609
-
In-depth profiling of miRNA regulation in the body wall of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus during skin ulceration syndrome progression.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018 Aug;79:202-208. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.05.020. Epub 2018 May 26. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29763733
-
MicroRNAs involved in innate immunity regulation in the sea cucumber: A review.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 Dec;95:297-304. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.10.049. Epub 2019 Oct 25. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31669896 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma Exosomal miRNA-122-5p and miR-300-3p as Potential Markers for Transient Ischaemic Attack in Rats.Front Aging Neurosci. 2018 Feb 6;10:24. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00024. eCollection 2018. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29467645 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Growth-Related Genes in Juvenile Chinese Sea Cucumber, Russian Sea Cucumber, and Their Hybrids.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2018 Apr;20(2):193-205. doi: 10.1007/s10126-018-9796-6. Epub 2018 Feb 28. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2018. PMID: 29492749
-
Small RNA Sequencing Based Identification of MiRNAs in Daphnia magna.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 14;10(9):e0137617. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137617. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26367422 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Expression of miRNAs in the Respiratory Tree of the Sea Cucumber Apostichopus japonicus Under Hypoxia Stress.G3 (Bethesda). 2017 Nov 6;7(11):3681-3692. doi: 10.1534/g3.117.1129. G3 (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 28916650 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell. 2004; 116: 281–297. - PubMed
-
- Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, Aharonov R, Gilad S, Barad O, et al. Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human microRNAs. Nat Genet. 2005; 37: 766–770. - PubMed
-
- Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, Anderson TA. Plant microRNA: a small regulatory molecule with big impact. Dev Biol. 2006; 289: 3–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

