Reward expectation regulates brain responses to task-relevant and task-irrelevant emotional words: ERP evidence
- PMID: 26245838
- PMCID: PMC4733331
- DOI: 10.1093/scan/nsv097
Reward expectation regulates brain responses to task-relevant and task-irrelevant emotional words: ERP evidence
Abstract
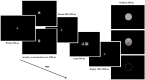
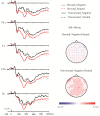
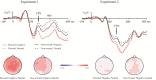
We investigated the effect of reward expectation on the processing of emotional words in two experiments using event-related potentials (ERPs). A cue indicating the reward condition of each trial (incentive vs non-incentive) was followed by the presentation of a negative or neutral word, the target. Participants were asked to discriminate the emotional content of the target word in Experiment 1 and to discriminate the color of the target word in Experiment 2, rendering the emotionality of the target word task-relevant in Experiment 1, but task-irrelevant in Experiment 2. The negative bias effect, in terms of the amplitude difference between ERPs for negative and neutral targets, was modulated by the task-set. In Experiment 1, P31 and early posterior negativity revealed a larger negative bias effect in the incentive condition than that in the non-incentive condition. However, in Experiment 2, P31 revealed a diminished negative bias effect in the incentive condition compared with that in the non-incentive condition. These results indicate that reward expectation improves top-down attentional concentration to task-relevant information, with enhanced sensitivity to the emotional content of target words when emotionality is task-relevant, but with reduced differential brain responses to emotional words when their content is task-irrelevant.
Keywords: reward expectation; emotional Stroop; negative bias; event-related potential.
© The Author (2015). Published by Oxford University Press. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential modulations of reward expectation on implicit facial emotion processing: ERP evidence.Psychophysiology. 2019 Mar;56(3):e13304. doi: 10.1111/psyp.13304. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Psychophysiology. 2019. PMID: 30443953
-
Task relevance regulates the interaction between reward expectation and emotion.Exp Brain Res. 2014 Jun;232(6):1783-91. doi: 10.1007/s00221-014-3870-8. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Exp Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24553754
-
Brain processing of task-relevant and task-irrelevant emotional words: an ERP study.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2014 Sep;14(3):939-50. doi: 10.3758/s13415-013-0247-6. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24481851
-
Interactions between reward motivation and emotional processing.Prog Brain Res. 2019;247:1-21. doi: 10.1016/bs.pbr.2019.03.023. Epub 2019 Apr 17. Prog Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31196430 Review.
-
Does reward modulate actions or bias attention?J Neurosci. 2007 Oct 10;27(41):10919-21. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2957-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17928432 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The influence of reward anticipation on conflict control in children and adolescents: Evidences from hierarchical drift-diffusion model and event-related potentials.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2022 Jun;55:101118. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2022.101118. Epub 2022 May 24. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35653919 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal Oxytocin Selectively Modulates Large-Scale Brain Networks in Humans.Brain Connect. 2017 Sep;7(7):454-463. doi: 10.1089/brain.2017.0528. Brain Connect. 2017. PMID: 28762756 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Neural correlates of reward-related response tendencies in an equiprobable Go/NoGo task.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2019 Jun;19(3):555-567. doi: 10.3758/s13415-019-00692-5. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30788804
-
Attention Capture of Non-target Emotional Faces: An Evidence From Reward Learning.Front Psychol. 2020 Jan 31;10:3004. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.03004. eCollection 2019. Front Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32082205 Free PMC article.
-
Halfhearted Action and Control.Ergo (Ann Arbor). 2017;4:09. doi: 10.3998/ergo.12405314.0004.009. Ergo (Ann Arbor). 2017. PMID: 29152537 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baines S., Ruz M., Rao A., Denison R., Nobre A.C. (2011). Modulation of neural activity by motivational and spatial biases. Neuropsychologia, 49, 2489–97. - PubMed
-
- Baxter M.G., Murray E.A. (2002). The amygdala and reward. Nature Review Neuroscience, 3, 563–73. - PubMed
-
- Bayer M., Sommer W., Schacht A. (2012). P1 and beyond: functional separation of multiple emotion effects in word recognition. Psychophysiology, 49, 959–69. - PubMed
-
- Becker E.S., Rinck M., Margraf J., Roth W.T. (2001). The emotional Stroop effect in anxiety disorders: general emotionality or disorder specificity? Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 15, 147–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

