Upregulated long non-coding RNA AFAP1-AS1 expression is associated with progression and poor prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PMID: 26246469
- PMCID: PMC4653014
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4057
Upregulated long non-coding RNA AFAP1-AS1 expression is associated with progression and poor prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Abstract
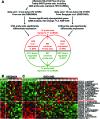
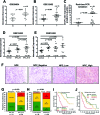
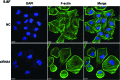
Altered expression of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) associated with human carcinogenesis. We performed a cDNA microarray analysis of lncRNA expression in 12 cases of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) and 4 non-tumor nasopharyngeal epitheliums. One lncRNA, actin filament associated protein 1 antisense RNA1 (AFAP1-AS1), was identified and selected for further study. AFAP1-AS1 expression was upregulated in NPC and associated with NPC metastasis and poor prognosis. In vitro experiments demonstrated that AFAP1-AS1 knockdown significantly inhibited the NPC cell migration and invasive capability. AFAP1-AS1 knockdown also increased AFAP1 protein expression. Proteomic and bioinformatics analyses suggested that AFAP1-AS1 affected the expression of several small GTPase family members and molecules in the actin cytokeratin signaling pathway. AFAP1-AS1 promoted cancer cell metastasis via regulation of actin filament integrity. AFAP1-AS1 might be a potential novel marker that can predict cancer patient prognosis and as a potential therapeutic target for NPC.
Keywords: AFAP1 antisense RNA1 (AFAP1-AS1); long non-coding RNA (LncRNA); metastasis; nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC); prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





References
-
- Wei WI, Sham JS. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 2005;365:2041–2054. - PubMed
-
- Chang ET, Adami HO. The enigmatic epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer epidemiology, biomarkers & prevention : a publication of the American Association for Cancer Research, cosponsored by the American Society of Preventive Oncology. 2006;15:1765–1777. - PubMed
-
- Lo KW, Chung GT, To KF. Deciphering the molecular genetic basis of NPC through molecular, cytogenetic, and epigenetic approaches. Semin Cancer Biol. 2012;22:79–86. - PubMed
-
- Xiong W, Zeng ZY, Xia JH, Xia K, Shen SR, Li XL, Hu DX, Tan C, Xiang JJ, Zhou J, Deng H, Fan SQ, Li WF, Wang R, Zhou M, Zhu SG, et al. A susceptibility locus at chromosome 3p21 linked to familial nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Research. 2004;64:1972–1974. - PubMed
-
- Zeng Z, Huang H, Huang L, Sun M, Yan Q, Song Y, Wei F, Bo H, Gong Z, Zeng Y, Li Q, Zhang W, Li X, Xiang B, Li X, Li Y, et al. Regulation network and expression profiles of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs and their potential target host genes in nasopharyngeal carcinomas. Science China Life sciences. 2014;57:315–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

