Constitutive Activation of Interleukin-13/STAT6 Contributes to Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Related Primary Effusion Lymphoma Cell Proliferation and Survival
- PMID: 26246572
- PMCID: PMC4580153
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01525-15
Constitutive Activation of Interleukin-13/STAT6 Contributes to Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Related Primary Effusion Lymphoma Cell Proliferation and Survival
Abstract
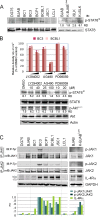
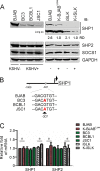
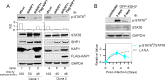
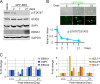
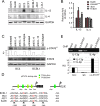
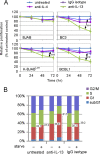
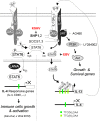
Activation of the Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) signaling pathway has been associated with numerous human malignancies, including primary effusion lymphomas (PELs). PEL, a cancerous proliferation of B cells, is caused by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV). Previously we identified constitutive phosphorylation of STAT6 on tyrosine 641 (p-STAT6(C)) in PEL cell lines BC3 and BCBL1; however, the molecular mechanism leading to this activation remains unclear. Here we demonstrate that STAT6 activation tightly correlates with interleukin-13 (IL-13) secretion, JAK1/2 tyrosine phosphorylation, and reduced expression of SHP1 due to KSHV infection. Moreover, p-STAT6(C) and reduction of SHP1 were also observed in KS patient tissue. Notably, blockade of IL-13 by antibody neutralization dramatically inhibits PEL cell proliferation and survival. Taken together, these results suggest that IL-13/STAT6 signaling is modulated by KSHV to promote host cell proliferation and viral pathogenesis.
Importance: STAT6 is a member of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) family, whose activation is linked to KSHV-associated cancers. The mechanism through which STAT6 is modulated by KSHV remains unclear. In this study, we demonstrated that constitutive activation of STAT6 in KSHV-associated PEL cells results from interleukin-13 (IL-13) secretion and reduced expression of SHP1. Importantly, we also found that depletion of IL-13 reduces PEL cell growth and survival. This discovery provides new insight that IL-13/STAT6 plays an essential role in KSHV pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nuclear Localization and Cleavage of STAT6 Is Induced by Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus for Viral Latency.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Jan 18;13(1):e1006124. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006124. eCollection 2017 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28099521 Free PMC article.
-
Altering the Anti-inflammatory Lipoxin Microenvironment: a New Insight into Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Pathogenesis.J Virol. 2016 Nov 28;90(24):11020-11031. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01491-16. Print 2016 Dec 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27681120 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus inhibits interleukin-4-mediated STAT6 phosphorylation to regulate apoptosis and maintain latency.J Virol. 2010 Nov;84(21):11134-44. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01293-10. Epub 2010 Aug 18. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20719954 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclooxygenase-2-prostaglandin E2-eicosanoid receptor inflammatory axis: a key player in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpes virus associated malignancies.Transl Res. 2013 Aug;162(2):77-92. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2013.03.004. Epub 2013 Apr 6. Transl Res. 2013. PMID: 23567332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Replication Machinery of Kaposi's Sarcoma-associated Herpesvirus and Drug Discovery Research].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019;139(1):69-73. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00164-2. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019. PMID: 30606932 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Kaposi Sarcoma Development.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 7;14(8):1869. doi: 10.3390/cancers14081869. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35454776 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of tristetraprolin on doxorubicin (adriamycin)-induced experimental kidney injury through inhibiting IL-13/STAT6 signal pathway.Am J Transl Res. 2020 Apr 15;12(4):1203-1221. eCollection 2020. Am J Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 32355536 Free PMC article.
-
A KSHV-targeted small molecule efficiently blocks SARS-CoV-2 infection via inhibiting expression of EGFR and Cyclin A2.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2025 Dec;14(1):2440490. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2024.2440490. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2025. PMID: 39655540 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Degradation by Gammaherpesvirus RTAs: More Than Just Viral Transactivators.Viruses. 2023 Mar 11;15(3):730. doi: 10.3390/v15030730. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36992439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of viral oncogenesis in haematological malignancies: perspectives from metabolic reprogramming, epigenetic regulation and immune microenvironment remodeling.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2025 May 10;14(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s40164-025-00655-2. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40349096 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Soulier J, Grollet L, Oksenhendler E, Cacoub P, Cazals-Hatem D, Babinet P, d'Agay MF, Clauvel JP, Raphael M, Degos L, Sigaux F. 1995. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in multicentric Castleman's disease. Blood 86:1276–1280. - PubMed
-
- Abend JR, Ramalingam D, Kieffer-Kwon P, Uldrick TS, Yarchoan R, Ziegelbauer JM. 2012. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus microRNAs target IRAK1 and MYD88, two components of the Toll-like receptor/interleukin-1R signaling cascade, to reduce inflammatory-cytokine expression. J Virol 86:11663–11674. doi:10.1128/JVI.01147-12. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

