Urine Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 and Lupus Nephritis Disease Activity: Preliminary Report of a Prospective Longitudinal Study
- PMID: 26246906
- PMCID: PMC4515289
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/962046
Urine Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 and Lupus Nephritis Disease Activity: Preliminary Report of a Prospective Longitudinal Study
Abstract
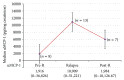
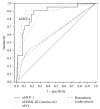
Objective. This longitudinal study aimed to determine the urine monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (uMCP-1) levels in patients with biopsy-proven lupus nephritis (LN) at various stages of renal disease activity and to compare them to current standard markers. Methods. Patients with LN-active or inactive-had their uMCP-1 levels and standard disease activity markers measured at baseline and 2 and 4 months. Urinary parameters, renal function test, serological markers, and renal SLE disease activity index-2K (renal SLEDAI-2K) were analyzed to determine their associations with uMCP-1. Results. A hundred patients completed the study. At each visit, uMCP-1 levels (pg/mg creatinine) were significantly higher in the active group especially with relapses and were significantly associated with proteinuria and renal SLEDAI-2K. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves showed that uMCP-1 was a potential biomarker for LN. Whereas multiple logistic regression analysis showed that only proteinuria and serum albumin and not uMCP-1 were independent predictors of LN activity. Conclusion. uMCP-1 was increased in active LN. Although uMCP-1 was not an independent predictor for LN activity, it could serve as an adjunctive marker when the clinical diagnosis of LN especially early relapse remains uncertain. Larger and longer studies are indicated.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Urinary MCP-1 and VCAM-1 as non-invasive biomarkers for the diagnosis and activity assessment of lupus nephritis.PLoS One. 2025 May 19;20(5):e0323334. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323334. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40388387 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-Inducible Protein 10 and Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 8;20(19):4954. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194954. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31597273 Free PMC article.
-
Urine Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1(UMCP-1) as a Biomarker of Renal Involvement in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2012 Nov;15(6):1191-5. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 23653850 Free PMC article.
-
Combined utilization of untimed single urine of MCP-1 and TWEAK as a potential indicator for proteinuria in lupus nephritis: A case-control study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Apr;97(16):e0343. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010343. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29668584 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal assessment of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in lupus nephritis as a biomarker of disease activity.Clin Rheumatol. 2016 Nov;35(11):2707-2714. doi: 10.1007/s10067-016-3404-9. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Clin Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 27624649
Cited by
-
Current Insights on Biomarkers in Lupus Nephritis: A Systematic Review of the Literature.J Clin Med. 2022 Sep 28;11(19):5759. doi: 10.3390/jcm11195759. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36233628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urinary MCP-1 and VCAM-1 as non-invasive biomarkers for the diagnosis and activity assessment of lupus nephritis.PLoS One. 2025 May 19;20(5):e0323334. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323334. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40388387 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-Inducible Protein 10 and Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 8;20(19):4954. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194954. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31597273 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary Biomarkers for Chronic Kidney Disease with a Focus on Gene Transcript.Chin Med J (Engl). 2017 Sep 20;130(18):2251-2256. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.213965. Chin Med J (Engl). 2017. PMID: 28875962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Use of Complement, Inflammation, and Fibrosis Biomarkers in Autoimmune Glomerulonephritis.Kidney Int Rep. 2020 Jul 23;5(10):1690-1699. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2020.07.018. eCollection 2020 Oct. Kidney Int Rep. 2020. PMID: 33102961 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chaib A., Mellilo N., Sangle S. R., et al. Antiphospholipid antibodies and increased bleeding complications following renal biopsy: a single centre study. Arthritis & Rheumatism. 2007;56(abstract supplement)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

