Comparative genomic analyses of transport proteins encoded within the genomes of Leptospira species
- PMID: 26247102
- PMCID: PMC4601928
- DOI: 10.1016/j.micpath.2015.07.019
Comparative genomic analyses of transport proteins encoded within the genomes of Leptospira species
Abstract
Select species of the bacterial genus Leptospira are causative agents of leptospirosis, an emerging global zoonosis affecting nearly one million people worldwide annually. We examined two Leptospira pathogens, Leptospira interrogans serovar Lai str. 56601 and Leptospira borgpetersenii serovar Hardjo-bovis str. L550, as well as the free-living leptospiral saprophyte, Leptospira biflexa serovar Patoc str. 'Patoc 1 (Ames)'. The transport proteins of these leptospires were identified and compared using bioinformatics to gain an appreciation for which proteins may be related to pathogenesis and saprophytism. L. biflexa possesses a disproportionately high number of secondary carriers for metabolite uptake and environmental adaptability as well as an increased number of inorganic cation transporters providing ionic homeostasis and effective osmoregulation in a rapidly changing environment. L. interrogans and L. borgpetersenii possess far fewer transporters, but those that they have are remarkably similar, with near-equivalent representation in most transporter families. These two Leptospira pathogens also possess intact sphingomyelinases, holins, and virulence-related outer membrane porins. These virulence-related factors, in conjunction with decreased transporter substrate versatility, indicate that pathogenicity was accompanied by progressively narrowing ecological niches and the emergence of a limited set of proteins responsible for host invasion. The variability of host tropism and mortality rates by infectious leptospires suggests that small differences in individual sets of proteins play important physiological and pathological roles.
Keywords: Genome analyses; Leptospira; Leptospirosis; Molecular transport; Pathogenesis; Spirochaetes.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
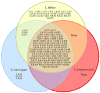
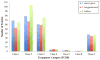
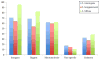
Similar articles
-
Comparative analyses of transport proteins encoded within the genomes of Leptospira species.Microb Pathog. 2016 Sep;98:118-31. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2016.06.013. Epub 2016 Jun 11. Microb Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27296707 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence of Leptospira santarosai serovar Shermani genome and prediction of virulence-associated genes.Gene. 2012 Dec 15;511(2):364-70. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.09.074. Epub 2012 Oct 3. Gene. 2012. PMID: 23041083
-
Comparison of Leptospira interrogans and Leptospira biflexa genomes: analysis of potential leptospiral-host interactions.Mol Biosyst. 2017 May 2;13(5):883-891. doi: 10.1039/c6mb00856a. Mol Biosyst. 2017. PMID: 28294222
-
Evolution and pathogenesis of Leptospira spp.: lessons learned from the genomes.Microbes Infect. 2009 Mar;11(3):328-33. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2008.12.007. Epub 2008 Dec 27. Microbes Infect. 2009. PMID: 19159695 Review.
-
New insights into the pathogenicity of leptospires: evasion of host defences.New Microbiol. 2010 Oct;33(4):283-92. New Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 21213586 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Analyses of Transport Proteins Encoded within the Genomes of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus HD100 and Bdellovibrio exovorus JSS.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017;27(6):332-349. doi: 10.1159/000484563. Epub 2017 Dec 7. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 29212086 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics of transport proteins in seven Bacteroides species.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 5;13(12):e0208151. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208151. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30517169 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics of the transportome of Ten Treponema species.Microb Pathog. 2019 Jul;132:87-99. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.04.034. Epub 2019 Apr 25. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31029716 Free PMC article.
-
Three Leptospira Strains From Western Indian Ocean Wildlife Show Highly Distinct Virulence Phenotypes Through Hamster Experimental Infection.Front Microbiol. 2019 Mar 11;10:382. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00382. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30915044 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic Leptospira: Advances in understanding the molecular pathogenesis and virulence.Open Vet J. 2018;8(1):13-24. doi: 10.4314/ovj.v8i1.4. Epub 2018 Jan 20. Open Vet J. 2018. PMID: 29445617 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bharti AR, Nally JE, Ricaldi JN, Matthias MA, Diaz MM, Lovett MA, et al. Leptospirosis: a zoonotic disease of global importance. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003;3:757–71. - PubMed
-
- Vinetz JM, Glass GE, Flexner CE, Mueller P, Kaslow DC. Sporadic urban leptospirosis. Ann Intern Med. 1996;125:794–8. - PubMed
-
- Toliver HL, Krane NK. Leptospirosis in New Orleans. The American journal of the medical sciences. 2014;347:159–63. - PubMed
-
- dos Paixao MS, Alves-Martin MF, da Tenorio MS, Starke-Buzetti WA, Alves ML, da Silva DT, et al. Serology, isolation, and molecular detection of Leptospira spp. from the tissues and blood of rats captured in a wild animal preservation centre in Brazil. Preventive veterinary medicine. 2014;115:69–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

