CaMKIIα-GluA1 Activity Underlies Vulnerability to Adolescent Binge Alcohol Drinking
- PMID: 26247621
- PMCID: PMC4558330
- DOI: 10.1111/acer.12819
CaMKIIα-GluA1 Activity Underlies Vulnerability to Adolescent Binge Alcohol Drinking
Abstract
Background: Binge drinking during adolescence is associated with increased risk for developing alcohol use disorders; however, the neural mechanisms underlying this liability are unclear. In this study, we sought to determine whether binge drinking alters expression or phosphorylation of 2 molecular mechanisms of neuroplasticity, calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II alpha (CaMKIIα) and the GluA1 subunit of AMPA receptors (AMPARs) in addiction-associated brain regions. We also asked whether activation of CaMKIIα-dependent AMPAR activity escalates binge-like drinking.
Methods: To address these questions, CaMKIIαT286 and GluA1S831 protein phosphorylation and expression were assessed in the amygdala and striatum of adolescent and adult male C57BL/6J mice immediately after voluntary binge-like alcohol drinking (blood alcohol >80 mg/dl). In separate mice, effects of the CaMKIIα-dependent GluA1S831 phosphorylation (pGluA1S831 )-enhancing drug tianeptine were tested on binge-like alcohol consumption in both age groups.
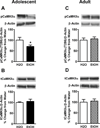
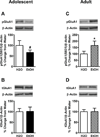
Results: Binge-like drinking decreased CaMKIIαT286 phosphorylation (pCaMKIIαT286 ) selectively in adolescent amygdala with no effect in adults. Alcohol also produced a trend for reduced pGluA1S831 expression in adolescent amygdala but differentially increased pGluA1S831 in adult amygdala. No effects were observed in the nucleus accumbens or dorsal striatum. Tianeptine increased binge-like alcohol consumption in adolescents but decreased alcohol consumption in adults. Sucrose consumption was similarly decreased by tianeptine pretreatment in both ages.
Conclusions: These data show that the adolescent and adult amygdalae are differentially sensitive to effects of binge-like alcohol drinking on plasticity-linked glutamate signaling molecules. Tianeptine-induced increases in binge-like drinking only in adolescents suggest that differential CaMKIIα-dependent AMPAR activation may underlie age-related escalation of binge drinking.
Keywords: Adolescence; Alcohol; Binge; CaMKII; GluA1.
Copyright © 2015 by the Research Society on Alcoholism.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Calcium-permeable AMPA receptor activity and GluA1 trafficking in the basolateral amygdala regulate operant alcohol self-administration.Addict Biol. 2021 Sep;26(5):e13049. doi: 10.1111/adb.13049. Epub 2021 May 5. Addict Biol. 2021. PMID: 33955100 Free PMC article.
-
Potentiation of amygdala AMPA receptor activity selectively promotes escalated alcohol self-administration in a CaMKII-dependent manner.Addict Biol. 2017 May;22(3):652-664. doi: 10.1111/adb.12357. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Addict Biol. 2017. PMID: 26742808 Free PMC article.
-
Moderate Alcohol Drinking and the Amygdala Proteome: Identification and Validation of Calcium/Calmodulin Dependent Kinase II and AMPA Receptor Activity as Novel Molecular Mechanisms of the Positive Reinforcing Effects of Alcohol.Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Mar 15;79(6):430-42. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.10.020. Epub 2014 Oct 31. Biol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 25579851 Free PMC article.
-
Sex- and age-dependent impacts of nicotine and ethanol binge drinking on the brain: Insights from preclinical research.J Neurochem. 2025 Feb;169(2):e16249. doi: 10.1111/jnc.16249. Epub 2024 Oct 24. J Neurochem. 2025. PMID: 39449196 Review.
-
Recent Perspectives on Sex Differences in Compulsion-Like and Binge Alcohol Drinking.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 6;22(7):3788. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073788. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33917517 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Age-related differences in the effect of chronic alcohol on cognition and the brain: a systematic review.Transl Psychiatry. 2022 Aug 25;12(1):345. doi: 10.1038/s41398-022-02100-y. Transl Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36008381 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of LHb CaMKII in the Comorbidity of Depressive and Alcohol Use Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 30;21(21):8123. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218123. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33143210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium-permeable AMPA receptor activity and GluA1 trafficking in the basolateral amygdala regulate operant alcohol self-administration.Addict Biol. 2021 Sep;26(5):e13049. doi: 10.1111/adb.13049. Epub 2021 May 5. Addict Biol. 2021. PMID: 33955100 Free PMC article.
-
Potentiation of amygdala AMPA receptor activity selectively promotes escalated alcohol self-administration in a CaMKII-dependent manner.Addict Biol. 2017 May;22(3):652-664. doi: 10.1111/adb.12357. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Addict Biol. 2017. PMID: 26742808 Free PMC article.
-
Individual Differences in Ethanol Drinking and Seeking Behaviors in Rats Exposed to Chronic Intermittent Ethanol Vapor Exposure is Associated with Altered CaMKII Autophosphorylation in the Nucleus Accumbens Shell.Brain Sci. 2019 Dec 11;9(12):367. doi: 10.3390/brainsci9120367. Brain Sci. 2019. PMID: 31835746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alaux-Cantin S, Warnault V, Legastelois R, Botia B, Pierrefiche O, Vilpoux C, Naassila M. Alcohol intoxications during adolescence increase motivation for alcohol in adult rats and induce neuroadaptations in the nucleus accumbens. Neuropharmacology. 2013;67:521–531. - PubMed
-
- Apergis-Schoute AM, Debiec J, Doyere V, Ledoux JE, Schafe GE. Auditory fear conditioning and long-term potentiation in the lateral amygdala require ERK/MAP kinase signaling in the auditory thalamus: a role for presynaptic plasticity in the fear system. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience. 2005;25:5730–5739. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barria A, Muller D, Derkach V, Griffith LC, Soderling TR. Regulatory phosphorylation of AMPA-type glutamate receptors by CaM-KII during long-term potentiation. Science. 1997;276:2042–2045. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

