Effects of Zidovudine Treatment on Heart mRNA Expression and Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number Associated with Alterations in Deoxynucleoside Triphosphate Composition in a Neonatal Rat Model
- PMID: 26248377
- PMCID: PMC4576025
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01180-15
Effects of Zidovudine Treatment on Heart mRNA Expression and Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number Associated with Alterations in Deoxynucleoside Triphosphate Composition in a Neonatal Rat Model
Abstract
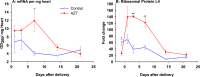
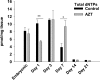
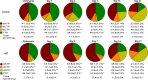
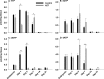
The prevention of mother-to-child transmission (MTCT) of HIV is a crucial component in HIV therapy. Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), primarily 3'-azido-3'-thymidine (AZT [zidovudine]), have been used to treat both mothers and neonates. While AZT is being replaced with less toxic drugs in treating mothers in MTCT prevention, it is still commonly used to treat neonates. Problems related to mitochondrial toxicity and potential mutagenesis associated with AZT treatment have been reported in treated cohorts. Yet little is known concerning the metabolism and potential toxicity of AZT on embryonic and neonatal tissues, especially considering that the enzymes of nucleoside metabolism change dramatically as many tissues convert from hyperplastic to hypertrophic growth during this period. AZT is known to inhibit thymidine phosphorylation and potentially alter deoxynucleoside triphosphate (dNTP) pools in adults. This study examines the effects of AZT on dNTP pools, mRNA expression of deoxynucleoside/deoxynucleotide metabolic enzymes, and mitochondrial DNA levels in a neonatal rat model. Results show that AZT treatment dramatically altered dNTP pools in the first 7 days of life after birth, which normalized to age-matched controls in the second and third weeks. Additionally, AZT treatment dramatically increased the mRNA levels of many enzymes involved in deoxynucleotide synthesis and mitochondrial biogenesis during the first week of life, which normalized to age-matched controls by the third week. These results were correlated with depletion of mitochondrial DNA noted in the second week. Taken together, results demonstrated that AZT treatment has a powerful effect on the deoxynucleotide synthesis pathways that may be associated with toxicity and mutagenesis.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Origin of pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotide pools in perfused rat heart: implications for 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine-dependent cardiotoxicity.Biochem J. 2009 Aug 27;422(3):513-20. doi: 10.1042/BJ20082427. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19558366
-
Mitochondrial toxicity in hearts of CD-1 mice following perinatal exposure to AZT, 3TC, or AZT/3TC in combination.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2007 Apr-May;48(3-4):190-200. doi: 10.1002/em.20191. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2007. PMID: 16395692
-
Phosphorylation of thymidine and AZT in heart mitochondria: elucidation of a novel mechanism of AZT cardiotoxicity.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2004;4(2):155-67. doi: 10.1385/ct:4:2:155. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2004. PMID: 15371631 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of genotoxicity of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2007 Apr-May;48(3-4):215-23. doi: 10.1002/em.20195. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2007. PMID: 16395695 Review.
-
AZT: an old drug with new perspectives.Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2008 Jan;3(1):20-37. doi: 10.2174/157488408783329913. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18690875 Review.
Cited by
-
Entecavir competitively inhibits deoxyguanosine and deoxyadenosine phosphorylation in isolated mitochondria and the perfused rat heart.J Biol Chem. 2022 May;298(5):101876. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101876. Epub 2022 Mar 28. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35358513 Free PMC article.
-
Complex Regulation of Mitochondrial Function During Cardiac Development.J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Jul 2;8(13):e012731. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012731. Epub 2019 Jun 19. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 31215339 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Connor EM, Sperling RS, Gelber R, Kiselev P, Scott G, O'Sullivan MJ, VanDyke R, Bey M, Shearer W, Jacobson RL. 1994. Reduction of maternal-infant transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 with zidovudine treatment. Pediatric AIDS Clinical Trials Group Protocol 076 Study Group. N Engl J Med 331:1173–1180. - PubMed
-
- Cooper ER, Charurat M, Mofenson L, Hanson IC, Pitt J, Diaz C, Hayani K, Handelsman E, Smeriglio V, Hoff R, Blattner W. 2002. Combination antiretroviral strategies for the treatment of pregnant HIV-1-infected women and prevention of perinatal HIV-1 transmission. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 29:484–494. doi:10.1097/00042560-200204150-00009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- WHO. 2010. Antiretroviral therapy for HIV infection in infants and children: towards universal access. Recommendations for a public health approach. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. - PubMed
-
- WHO. 2013. Consolidated guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection: recommendations for a public health approach, June 2013. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

