Prognostic Value of Model for End-Stage Liver Disease Score Measurements on a Daily Basis in Critically Ill Patients With Cirrhosis
- PMID: 26249009
- PMCID: PMC4567441
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2015.06.017
Prognostic Value of Model for End-Stage Liver Disease Score Measurements on a Daily Basis in Critically Ill Patients With Cirrhosis
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether daily measurement of Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score adds prognostic value to the initial MELD score in predicting mortality among patients with cirrhosis admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU).
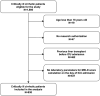
Methods: We included 830 consecutive patients with cirrhosis admitted to a tertiary care ICU from January 1, 2003, through December 31, 2013, who had MELD scores on admission day 1 (MELD-D1). Daily MELD score during the first 7 days of ICU admission were retrospectively abstracted. The performances of MELD-D1 to MELD-D7 and changes in MELD score on consecutive days (Δ-MELD) in predicting 90-day mortality were determined using logistic regression.
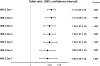
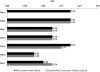
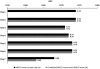
Results: MELD-D1 was an independent predictor of mortality (adjusted odds ratio, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.05-1.10; P<.001), with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.72. MELD-D2 to MELD-D7 yielded comparable performance to MELD-D1 with an approximately 10% increase in risk of death per each incremental unit of MELD score (odds ratios, 1.09-1.11; P<.001; AUCs, 0.68-0.72). Δ-MELD-D2 to Δ-MELD-D7 were not independently associated with mortality (P=.69, P=.42, P=.81, P=.94, P=.83 and P=.28, respectively) and did not increase the predictive performance (AUCs) when combined with MELD-D2 to MELD-D7.
Conclusion: Repeating MELD score assessment during the first 7 days after ICU admission does not improve the ability of the initial MELD score for predicting 90-day mortality among patients with cirrhosis. Our finding does not support the practice of routine daily measurement of the MELD score.
Copyright © 2015 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bicarbonate can improve the prognostic value of the MELD score for critically ill patients with cirrhosis.Ren Fail. 2014 Jul;36(6):889-94. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2014.894765. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Ren Fail. 2014. PMID: 24601755
-
Model for End-Stage Liver Disease score for predicting outcome in critically ill medical patients with liver cirrhosis.J Crit Care. 2012 Aug;27(4):424.e1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2011.11.014. Epub 2012 Jan 9. J Crit Care. 2012. PMID: 22227088
-
Factors that predict short-term intensive care unit mortality in patients with cirrhosis.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Sep;11(9):1194-1200.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.03.035. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23602820 Free PMC article.
-
Model for End-Stage Liver Disease score predicts mortality in critically ill cirrhotic patients.J Crit Care. 2014 Oct;29(5):881.e7-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2014.05.013. Epub 2014 May 28. J Crit Care. 2014. PMID: 24974049 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of Mortality in the Critically Ill Cirrhotic Patient: Is the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease Enough?J Am Coll Surg. 2017 Mar;224(3):276-282. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2016.11.005. Epub 2016 Nov 22. J Am Coll Surg. 2017. PMID: 27887981 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Predictive power of Model for End-Stage Liver Disease and Child-Turcotte-Pugh score for mortality in cirrhotic patients.Clin Exp Hepatol. 2018 Dec;4(4):240-246. doi: 10.5114/ceh.2018.80125. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Clin Exp Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 30603671 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Olson JC, Wendon JA, Kramer DJ, et al. Intensive care of the patient with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2011;54(5):1864–1872. - PubMed
-
- Foreman MG, Mannino DM, Moss M. Cirrhosis as a risk factor for sepsis and death: analysis of the National Hospital Discharge Survey. Chest. 2003;124(3):1016–1020. - PubMed
-
- Karvellas CJ, Bagshaw SM. Advances in management and prognostication in critically ill cirrhotic patients. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2014;20(2):210–217. - PubMed
-
- Munoz SJ, Stravitz RT, Gabriel DA. Coagulopathy of acute liver failure. Clin Liver Dis. 2009;13(1):95–107. - PubMed
-
- Chiou WL, Hsu FH. Pharmacokinetics of creatinine in man and its implications in the monitoring of renal function and in dosage regimen modifications in patients with renal insufficiency. J Clin Pharmacol. 1975;15(5-6):427–434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

