Noncoding RNAs and chronic inflammation: Micro-managing the fire within
- PMID: 26249326
- PMCID: PMC5054901
- DOI: 10.1002/bies.201500054
Noncoding RNAs and chronic inflammation: Micro-managing the fire within
Abstract
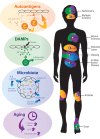
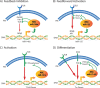
Inflammatory responses are essential for the clearance of pathogens and the repair of injured tissues; however, if these responses are not properly controlled chronic inflammation can occur. Chronic inflammation is now recognized as a contributing factor to many age-associated diseases including metabolic disorders, arthritis, neurodegeneration, and cardiovascular disease. Due to the connection between chronic inflammation and these diseases, it is essential to understand underlying mechanisms behind this process. In this review, factors that contribute to chronic inflammation are discussed. Further, we emphasize the emerging roles of microRNAs (miRNAs) and other noncoding RNAs (ncRNA) in regulating chronic inflammatory states, making them important future diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets.
Keywords: aging; autoimmunity; chronic inflammation; miRNAs; noncoding RNA.
© 2015 The Authors. BioEssays published by WILEY Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
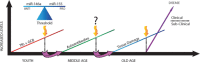
References
-
- Medzhitov R. 2008. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 454: 428–35. - PubMed
-
- Choy EH, Panayi GS. 2001. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 344: 907–16. - PubMed
-
- Arbuckle MR, McClain MT, Rubertone MV, Scofield RH, et al. 2003. Development of autoantibodies before the clinical onset of systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 349: 1526–33. - PubMed
-
- Ross CA, Poirier MA. 2004. Protein aggregation and neurodegenerative disease. Nat Med 10: 10–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

