Purification and crystallographic analysis of a FAD-dependent halogenase from Streptomyces sp. JCM9888
- PMID: 26249684
- PMCID: PMC4528926
- DOI: 10.1107/S2053230X15009929
Purification and crystallographic analysis of a FAD-dependent halogenase from Streptomyces sp. JCM9888
Abstract
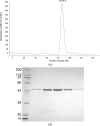
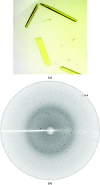
A new FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide)-dependent halogenase HalY from Streptomyces sp. JCM9888 was reported to be involved in the regioselective halogenation of adenine. HalY is a variant B FAD-dependent halogenase that is most similar to the halogenase PltA involved in pyoluteorin biosynthesis. This study reports the overexpression and purification of HalY with an N-terminal hexahistidine tag, followed by crystallization experiments and X-ray crystallographic analysis. HalY was purified as a monomer in solution and crystallized to give X-ray diffraction to a resolution of 1.7 Å. The crystal belonged to the monoclinic space group P21, with unit-cell parameters a = 41.4, b = 113.4, c = 47.6 Å, α = γ = 90, β = 107.4°, and contained one monomer of HalY in the asymmetric unit, with a calculated Matthews coefficient of 2.3 Å(3) Da(-1) and a solvent content of 46%. The structure of the halogenase CndH was used as a search model in molecular replacement to obtain the initial model of HalY. Manual model building and structure refinement of HalY are in progress.
Keywords: FAD-dependent halogenase; adenine; regioselective halogenation.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

