Crystallographic analysis of the N-terminal domain of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus nucleocapsid protein
- PMID: 26249685
- PMCID: PMC4528927
- DOI: 10.1107/S2053230X15010146
Crystallographic analysis of the N-terminal domain of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus nucleocapsid protein
Abstract
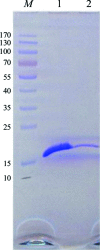
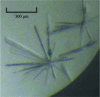
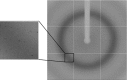
The N-terminal domain of the nucleocapsid protein from Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV NP-NTD) contains many positively charged residues and has been identified to be responsible for RNA binding during ribonucleocapsid formation by the virus. In this study, the crystallization and crystallographic analysis of MERS-CoV NP-NTD (amino acids 39-165), with a molecular weight of 14.7 kDa, are reported. MERS-CoV NP-NTD was crystallized at 293 K using PEG 3350 as a precipitant and a 94.5% complete native data set was collected from a cooled crystal at 77 K to 2.63 Å resolution with an overall Rmerge of 9.6%. The crystals were monoclinic and belonged to space group P21, with unit-cell parameters a = 35.60, b = 109.64, c = 91.99 Å, β = 101.22°. The asymmetric unit contained four MERS-CoV NP-NTD molecules.
Keywords: Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus; N-terminal domain; RNA binding; nucleocapsid protein.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of the N-terminal domain of human coronavirus OC43 nucleocapsid protein.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2010 Jul 1;66(Pt 7):815-8. doi: 10.1107/S1744309110017616. Epub 2010 Jun 24. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2010. PMID: 20606281 Free PMC article.
-
Structural characterization of the N-terminal part of the MERS-CoV nucleocapsid by X-ray diffraction and small-angle X-ray scattering.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2016 Feb;72(Pt 2):192-202. doi: 10.1107/S2059798315024328. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2016. PMID: 26894667 Free PMC article.
-
Ribonucleocapsid formation of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus through molecular action of the N-terminal domain of N protein.J Virol. 2007 Apr;81(8):3913-21. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02236-06. Epub 2007 Jan 17. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17229691 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning, expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of the structural domain of the nucleocapsid N protein from porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV).Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2003 Aug;59(Pt 8):1504-6. doi: 10.1107/s0907444903012721. Epub 2003 Jul 23. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2003. PMID: 12876367
-
Solution structure of the c-terminal dimerization domain of SARS coronavirus nucleocapsid protein solved by the SAIL-NMR method.J Mol Biol. 2008 Jul 18;380(4):608-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.11.093. Epub 2007 Dec 5. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18561946 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Targeting the N-Terminus Domain of the Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Protein Induces Abnormal Oligomerization via Allosteric Modulation.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Apr 19;9:871499. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.871499. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35517857 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of development of multi-epitope vaccine against Middle East respiratory syndrome using in silico approach.Infect Drug Resist. 2018 Nov 21;11:2377-2391. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S175114. eCollection 2018. Infect Drug Resist. 2018. PMID: 30538505 Free PMC article.
-
Recent insights into the development of therapeutics against coronavirus diseases by targeting N protein.Drug Discov Today. 2016 Apr;21(4):562-72. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2015.11.015. Epub 2015 Dec 12. Drug Discov Today. 2016. PMID: 26691874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An overview of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus vaccines in preclinical studies.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2020 Sep;19(9):817-829. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2020.1813574. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2020. PMID: 32842811 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen, Y.-W., Jhan, C.-R., Neidle, S. & Hou, M.-H. (2014). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 10682–10686. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

