Sex hormones have pervasive effects on thymic epithelial cells
- PMID: 26250469
- PMCID: PMC4528223
- DOI: 10.1038/srep12895
Sex hormones have pervasive effects on thymic epithelial cells
Abstract
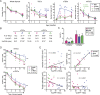
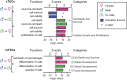
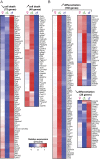
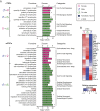
The goal of our study was to evaluate at the systems-level, the effect of sex hormones on thymic epithelial cells (TECs). To this end, we sequenced the transcriptome of cortical and medullary TECs (cTECs and mTECs) from three groups of 6 month-old mice: males, females and males castrated at four weeks of age. In parallel, we analyzed variations in the size of TEC subsets in those three groups between 1 and 12 months of age. We report that sex hormones have pervasive effects on the transcriptome of TECs. These effects were exquisitely TEC-subset specific. Sexual dimorphism was particularly conspicuous in cTECs. Male cTECs displayed low proliferation rates that correlated with low expression of Foxn1 and its main targets. Furthermore, male cTECs expressed relatively low levels of genes instrumental in thymocyte expansion (e.g., Dll4) and positive selection (Psmb11 and Ctsl). Nevertheless, cTECs were more abundant in males than females. Accumulation of cTECs in males correlated with differential expression of genes regulating cell survival in cTECs and cell differentiation in mTECs. The sexual dimorphism of TECs highlighted here may be mechanistically linked to the well-recognized sex differences in susceptibility to infections and autoimmune diseases.
Figures

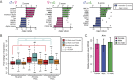
References
-
- Whitacre C. C. Sex differences in autoimmune disease. Nat Immunol 2, 777–780 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Markle J. G. & Fish E. N. SeXX matters in immunity. Trends Immunol. 35, 97–104 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Danska J. S. Sex matters for mechanism. Sci Transl Med 6, 258fs40 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Markle J. G. et al. Sex differences in the gut microbiome drive hormone-dependent regulation of autoimmunity. Science 339, 1084–1088 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

