Magnetic Alignment of Microelements Containing Cultured Neuronal Networks for High-Throughput Screening
- PMID: 26250488
- PMCID: PMC4852856
- DOI: 10.1177/1087057115598609
Magnetic Alignment of Microelements Containing Cultured Neuronal Networks for High-Throughput Screening
Abstract
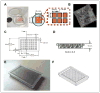
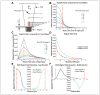
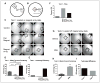
High-throughput screening (HTS) on neurons presents unique difficulties because they are postmitotic, limited in supply, and challenging to harvest from animals or generate from stem cells. These limitations have hindered neurological drug discovery, leaving an unmet need to develop cost-effective technology for HTS using neurons. Traditional screening methods use up to 20,000 neurons per well in 384-well plates. To increase throughput, we use "microraft" arrays, consisting of 1600 square, releasable, paramagnetic, polystyrene microelements (microrafts), each providing a culture surface for 500-700 neurons. These microrafts can be detached from the array and transferred to 384-well plates for HTS; however, they must be centered within wells for automated imaging. Here, we developed a magnet array plate, compatible with HTS fluid-handling systems, to center microrafts within wells. We used finite element analysis to select an effective size of the magnets and confirmed that adjacent magnetic fields do not interfere. We then experimentally tested the plate's centering ability and found a centering efficiency of 100%, compared with 4.35% using a flat magnet. We concluded that microrafts could be centered after settling randomly within the well, overcoming friction, and confirmed these results by centering microrafts containing hippocampal neurons cultured for 8 days.
Keywords: finite element analysis; high-throughput screening; magnetic centering; microfabrication; microraft arrays; primary neurons.
© 2015 Society for Laboratory Automation and Screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: NLA and YW are inventors (Patent No. 20130066031) and have financial interest in Cell Microsystems, Inc. AMT has financial interest in Xona Microfluidics, LLC. KG declares no competing financial interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A technology of a different sort: microraft arrays.Lab Chip. 2021 Sep 7;21(17):3204-3218. doi: 10.1039/d1lc00506e. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Lab Chip. 2021. PMID: 34346456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-throughput screening in primary neurons.Methods Enzymol. 2012;506:331-60. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-391856-7.00041-X. Methods Enzymol. 2012. PMID: 22341232 Free PMC article.
-
Automated microraft platform to identify and collect non-adherent cells successfully gene-edited with CRISPR-Cas9.Biosens Bioelectron. 2017 May 15;91:175-182. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.12.019. Epub 2016 Dec 10. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017. PMID: 28006686 Free PMC article.
-
Plate reader-based assays for measuring cell viability, neuroprotection and calcium in primary neuronal cultures.J Neurosci Methods. 2012 Jan 15;203(1):141-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2011.09.007. Epub 2011 Sep 24. J Neurosci Methods. 2012. PMID: 21968036 Free PMC article.
-
Primary cells and stem cells in drug discovery: emerging tools for high-throughput screening.Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2011 Apr;9(2):108-24. doi: 10.1089/adt.2010.0305. Epub 2010 Dec 27. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2011. PMID: 21186936 Review.
Cited by
-
Selective single cell isolation for genomics using microraft arrays.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Sep 30;44(17):8292-301. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw700. Epub 2016 Aug 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27530426 Free PMC article.
-
Automated sensing and splitting of stem cell colonies on microraft arrays.APL Bioeng. 2019 Aug 29;3(3):036106. doi: 10.1063/1.5113719. eCollection 2019 Sep. APL Bioeng. 2019. PMID: 31489396 Free PMC article.
-
A technology of a different sort: microraft arrays.Lab Chip. 2021 Sep 7;21(17):3204-3218. doi: 10.1039/d1lc00506e. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Lab Chip. 2021. PMID: 34346456 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang MH, Luo GR, Zhou YJ, et al. Phenotypic Screens Targeting Neurodegenerative Diseases. J Biomol Screen. 2014;19(1):1–16. - PubMed
-
- An WF, Tolliday NJ. Introduction. In: Clemons PA, Tolliday NJ, Wagner BK, editors. Cell-Based Assays for High Throughput Screening: Methods and Protocols. Human Press; New York: 2009. - PubMed
-
- Götte M, Hofmann G, Michou-Gallani AI, et al. An Imaging Assay to Analyze Primary Neurons for Cellular Neurotoxicity. J Neurosci Methods. 2010;192(1):7–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

