Kidney Function and Fracture Risk: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study
- PMID: 26250781
- PMCID: PMC4724513
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.06.020
Kidney Function and Fracture Risk: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study
Abstract
Background: People with end-stage renal disease are at high risk for bone fracture. Less is known about fracture risk in milder chronic kidney disease and whether chronic kidney disease-associated fracture risk varies by sex or assessment with alternative kidney markers.
Study design: Prospective cohort study.
Setting & participants: 10,955 participants from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study followed up from 1996 to 2011.
Predictor: Kidney function as assessed by creatinine-based estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFRcr), urine albumin-creatinine ratio, and alternative filtration markers.
Outcomes: Fracture-related hospitalizations determined by diagnostic code.
Measurements: Baseline kidney markers; hospitalizations identified by self-report during annual telephone contact and active surveillance of local hospital discharge lists.
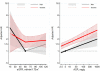
Results: Mean age of participants was 63 years, 56% were women, and 22% were black. During a median follow-up of 13 years, there were 722 incident fracture-related hospitalizations. Older age, female sex, and white race were associated with higher risk for fracture (P<0.001). The relationship between eGFRcr and fracture risk was nonlinear: <60mL/min/1.73m(2), lower eGFRcr was associated with higher fracture risk (adjusted HR per 10mL/min/1.73m(2) lower, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.05-1.47); there was no statistically significant association for ≥60mL/min/1.73m(2) in the primary analysis. In contrast, there was a graded association between other markers of kidney function and subsequent fracture, including albumin-creatinine ratio (HR per doubling, 1.10; 95% CI, 1.06-1.14), cystatin C-based eGFR (HR per 1-SD decrease, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.06-1.25), and 1/β2-microglobulin (HR per 1-SD decrease, 1.26, 95% CI, 1.15-1.37).
Limitations: No bone mineral density assessment; one-time measurement of kidney function.
Conclusions: Both low eGFR and higher albuminuria were significant risk factors for fracture in this community-based population. The shape of the association in the upper ranges of eGFR varied by the filtration marker used in estimation.
Keywords: Bone fracture; albumin-creatinine ratio (ACR); albuminuria; chronic kidney disease (CKD); estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR); fracture risk; hospitalization; hospitalized fracture; kidney filtration markers; renal function.
Copyright © 2016 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Jadoul M, Albert JM, Akiba T, et al. Incidence and risk factors for hip or other bone fractures among hemodialysis patients in the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study. Kidney Int. 2006;70(7):1358–1366. - PubMed
-
- Jorgensen L, Jenssen T, Ahmed L, Bjornerem A, Joakimsen R, Jacobsen BK. Albuminuria and risk of nonvertebral fractures. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167(13):1379–1385. - PubMed
-
- Levin A, Stevens PE. Summary of KDIGO 2012 CKD Guideline: behind the scenes, need for guidance, and a framework for moving forward. Kidney Int. 2014;85(1):49–61. - PubMed
-
- Levey AS, Coresh J. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet. 2012;379(9811):165–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK089174/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08DK092287/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK106414/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK092287/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

