Radiomic feature clusters and prognostic signatures specific for Lung and Head & Neck cancer
- PMID: 26251068
- PMCID: PMC4937496
- DOI: 10.1038/srep11044
Radiomic feature clusters and prognostic signatures specific for Lung and Head & Neck cancer
Abstract
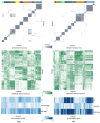
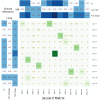
Radiomics provides a comprehensive quantification of tumor phenotypes by extracting and mining large number of quantitative image features. To reduce the redundancy and compare the prognostic characteristics of radiomic features across cancer types, we investigated cancer-specific radiomic feature clusters in four independent Lung and Head &Neck (H) cancer cohorts (in total 878 patients). Radiomic features were extracted from the pre-treatment computed tomography (CT) images. Consensus clustering resulted in eleven and thirteen stable radiomic feature clusters for Lung and H cancer, respectively. These clusters were validated in independent external validation cohorts using rand statistic (Lung RS = 0.92, p < 0.001, H RS = 0.92, p < 0.001). Our analysis indicated both common as well as cancer-specific clustering and clinical associations of radiomic features. Strongest associations with clinical parameters: Prognosis Lung CI = 0.60 ± 0.01, Prognosis H CI = 0.68 ± 0.01; Lung histology AUC = 0.56 ± 0.03, Lung stage AUC = 0.61 ± 0.01, H HPV AUC = 0.58 ± 0.03, H stage AUC = 0.77 ± 0.02. Full utilization of these cancer-specific characteristics of image features may further improve radiomic biomarkers, providing a non-invasive way of quantifying and monitoring tumor phenotypic characteristics in clinical practice.
Figures


References
-
- Chung C. H., Levy S., Chaurand P. & Carbone D. P. Genomics and proteomics: emerging technologies in clinical cancer research. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hemat. 61, 1–25 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Buckler A. J., Bresolin L., Dunnick N. R. & Sullivan D. C. A collaborative enterprise for multi-stakeholder participation in the advancement of quantitative imaging. Radiology 258, 906–914 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

