Glutamine Supplementation in Intensive Care Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials
- PMID: 26252319
- PMCID: PMC4616616
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001319
Glutamine Supplementation in Intensive Care Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials
Abstract
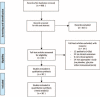
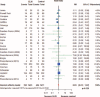
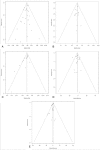
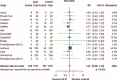
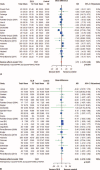
The role of glutamine (GLN) supplementation in critically ill patients is controversial. Our aim was to analyze its potential effect in patients admitted to intensive care unit (ICU).We performed a systematic literature review through Medline, Embase, Pubmed, Scopus, Ovid, ISI Web of Science, and the Cochrane-Controlled Trials Register searching for randomized clinical trials (RCTs) published from 1983 to 2014 and comparing GLN supplementation to no supplementation in patients admitted to ICU. A random-effect meta-analysis for each outcome (hospital and ICU mortality and rate of infections) of interest was carried out. The effect size was estimated by the risk ratio (RR).Thirty RCTs were analyzed with a total of 3696 patients, 1825 (49.4%) receiving GLN and 1859 (50.6%) no GLN (control groups). Hospital mortality rate was 27.6% in the GLN patients and 28.6% in controls with an RR of 0.93 (95% CI = 0.81-1.07; P = 0.325, I = 10.7%). ICU mortality was 18.0 % in the patients receiving GLN and 17.6% in controls with an RR of 1.01 (95% CI = 0.86-1.19; P = 0.932, I = 0%). The incidence of infections was 39.7% in GLN group versus 41.7% in controls. The effect of GLN was not significant (RR = 0.88; 95% CI = 0.76-1.03; P = 0.108, I = 56.1%).These results do not allow to recommend GLN supplementation in a generic population of critically ills. Further RCTs are needed to explore the effect of GLN in more specific cohort of patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Preiser JC, Wernerman J. Glutamine, a life-saving nutrient, but why? Crit Care Med 2003; 31:2555–2556. - PubMed
-
- Coeffier M, Dechelotte P. The role of glutamine in intensive care unit patients: mechanisms of action and clinical outcome. Nutr Rev 2005; 63:65–69. - PubMed
-
- Oudermans-van Straaten HM, Bosman RJ, Treskes M, et al. Plasma glutamine depletion and patient outcome in acute ICU admissions. Intensive Care Med 2001; 27:84–90. - PubMed
-
- Wischmeyer PE. Glutamine: role in critical illness and ongoing clinical trials. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2008; 24:190–197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

