Human respiratory syncytial virus non-structural protein NS1 modifies miR-24 expression via transforming growth factor-β
- PMID: 26253191
- PMCID: PMC4806578
- DOI: 10.1099/jgv.0.000261
Human respiratory syncytial virus non-structural protein NS1 modifies miR-24 expression via transforming growth factor-β
Abstract
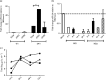
Human respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a major health challenge in the young and elderly owing to the lack of a safe and effective vaccine and proven antiviral drugs. Understanding the mechanisms by which viral genes and proteins modulate the host response to infection is critical for identifying novel disease intervention strategies. In this study, the RSV non-structural protein NS1 was shown to suppress miR-24 expression during infection. Lack of NS1 was linked to increased expression of miR-24, whilst NS1 overexpression suppressed miR-24 expression. NS1 was found to induce Kruppel-like factor 6 (KLF6), a transcription factor that positively regulates the transforming growth factor (TGF)-b pathway to induce cell cycle arrest. Silencing of KLF6 led to increased miR-24 expression via downregulation of TGF-β. Treatment with exogenous TGF-β suppressed miR-24 expression and induced KLF6. Confocal microscopy showed co-localization of KLF6 and RSV NS1. These findings indicated that RSV NS1 interacts with KLF6 and modulates miR-24 expression and TGF-β, which facilitates RSV replication.
Figures



References
-
- Basak A., Zhong M., Munzer J.S., Chrétien M., Seidah N.G. (2001). Implication of the proprotein convertases furin, PC5 and PC7 in the cleavage of surface glycoproteins of Hong Kong, Ebola and respiratory syncytial viruses: a comparative analysis with fluorogenic peptides Biochem J 353 537–545 10.1042/0264-6021:3530537 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

