Cumulin, an Oocyte-secreted Heterodimer of the Transforming Growth Factor-β Family, Is a Potent Activator of Granulosa Cells and Improves Oocyte Quality
- PMID: 26254468
- PMCID: PMC4583026
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.671487
Cumulin, an Oocyte-secreted Heterodimer of the Transforming Growth Factor-β Family, Is a Potent Activator of Granulosa Cells and Improves Oocyte Quality
Abstract
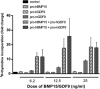
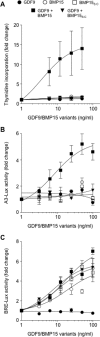
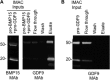
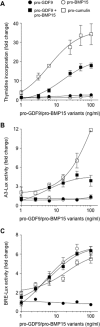
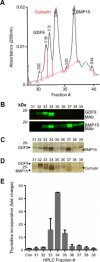
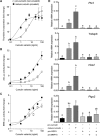
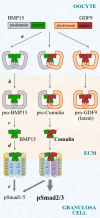
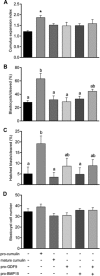
Growth differentiation factor 9 (GDF9) and bone morphogenetic protein 15 (BMP15) are oocyte-specific growth factors with central roles in mammalian reproduction, regulating species-specific fecundity, ovarian follicular somatic cell differentiation, and oocyte quality. In the human, GDF9 is produced in a latent form, the mechanism of activation being an open question. Here, we produced a range of recombinant GDF9 and BMP15 variants, examined their in silico and physical interactions and their effects on ovarian granulosa cells (GC) and oocytes. We found that the potent synergistic actions of GDF9 and BMP15 on GC can be attributed to the formation of a heterodimer, which we have termed cumulin. Structural modeling of cumulin revealed a dimerization interface identical to homodimeric GDF9 and BMP15, indicating likely formation of a stable complex. This was confirmed by generation of recombinant heterodimeric complexes of pro/mature domains (pro-cumulin) and covalent mature domains (cumulin). Both pro-cumulin and cumulin exhibited highly potent bioactivity on GC, activating both SMAD2/3 and SMAD1/5/8 signaling pathways and promoting proliferation and expression of a set of genes associated with oocyte-regulated GC differentiation. Cumulin was more potent than pro-cumulin, pro-GDF9, pro-BMP15, or the two combined on GC. However, on cumulus-oocyte complexes, pro-cumulin was more effective than all other growth factors at notably improving oocyte quality as assessed by subsequent day 7 embryo development. Our results support a model of activation for human GDF9 dependent on cumulin formation through heterodimerization with BMP15. Oocyte-secreted cumulin is likely to be a central regulator of fertility in mono-ovular mammals.
Keywords: IVM; SMAD transcription factor; bone morphogenetic protein (BMP); cumulin; cumulus granulosa cell; growth differentiation factor; oocyte quality; protein assembly; protein secretion; transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β).
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- McNatty K. P., Moore L. G., Hudson N. L., Quirke L. D., Lawrence S. B., Reader K., Hanrahan J. P., Smith P., Groome N. P., Laitinen M., Ritvos O., Juengel J. L. (2004) The oocyte and its role in regulating ovulation rate: a new paradigm in reproductive biology. Reproduction 128, 379–386 - PubMed
-
- Gilchrist R. B., Lane M., Thompson J. G. (2008) Oocyte-secreted factors: regulators of cumulus cell function and oocyte quality. Hum. Reprod. Update 14, 159–177 - PubMed
-
- Simpson C. M., Stanton P. G., Walton K. L., Chan K. L., Ritter L. J., Gilchrist R. B., Harrison C. A. (2012) Activation of latent human GDF9 by a single residue change (Gly 391 Arg) in the mature domain. Endocrinology 153, 1301–1310 - PubMed
-
- Al-Musawi S. L., Walton K. L., Heath D., Simpson C. M., Harrison C. A. (2013) Species differences in the expression and activity of bone morphogenetic protein 15. Endocrinology 154, 888–899 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

