The dilemma of stump appendicitis - A case report and literature review
- PMID: 26255005
- PMCID: PMC4573603
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2015.07.017
The dilemma of stump appendicitis - A case report and literature review
Abstract
Introduction: Stump appendicitis is one of the rare delayed complications post appendectomy with a reported incidence of 1 in 50,000 cases. Stump appendicitis can present as a diagnostic dilemma if the treating clinician is unfamiliar with this rare clinical entity. A PubMed search was conducted to identify cases of stump appendicitis following appendectomy. Sixty one cases of SA that were reported in English medical literature were analyzed.
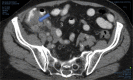
Presentation of case: We report a case of stump appendicitis (SA) with a systematic review and challenges encountered during the management.
Discussion: The interval from original appendectomy to stump appendicitis ranged from 4 days to 50 years. SA followed appendectomy in 58% of open and 31.6% of laparoscopic procedures. SA was frequently misdiagnosed as constipation, gastroenteritis or right sided diverticulitis, therefore leading to a significant delay to surgery. Computerized Tomography diagnosed SA in 56.3% of cases. Perforation with gangrene of the stump occurred in 60%.
Conclusion: Stump appendicitis can represent a diagnostic dilemma if the treating physician is unfamiliar with this uncommon clinical entity. Radiological imaging is required to aid diagnosis and a completion appendectomy is the modality of treatment.
Keywords: Appendectomy; Appendicectomy; Completion appendectomy; Stump appendicitis.
Crown Copyright © 2015. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inflammation of the residual appendix stump: a systematic review.Colorectal Dis. 2012 Mar;14(3):282-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1318.2010.02487.x. Colorectal Dis. 2012. PMID: 21054746
-
Stump appendicitis: A rare clinical entity.J Minim Access Surg. 2013 Oct;9(4):173-6. doi: 10.4103/0972-9941.118835. J Minim Access Surg. 2013. PMID: 24250064 Free PMC article.
-
A rare clinical entity: stump appendicitis. Case report and complete review of literature.Clin Ter. 2019 Nov-Dec;170(6):e409-e417. doi: 10.7417/CT.2019.2167. Clin Ter. 2019. PMID: 31696901 Review.
-
Stump appendicitis: a rare and unusual complication after appendectomy. Case report and review of the literature.Ann Ital Chir. 2014 Apr 7;85(ePub):S2239253X14022270. Ann Ital Chir. 2014. PMID: 25027013 Review.
-
Stump appendicitis after laparoscopic appendectomy; laparoscopic management and literature review.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021 Jul;84:106156. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2021.106156. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34229211 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
SpyGlass/Cholangioscope-Assisted Colonoscopic Removal of Appendicolith as a Nonsurgical Alternative for Stump Appendicitis Management.ACG Case Rep J. 2024 Jul 12;11(7):e01430. doi: 10.14309/crj.0000000000001430. eCollection 2024 Jul. ACG Case Rep J. 2024. PMID: 39006052 Free PMC article.
-
Point-of-care ultrasound diagnosis of stump appendicitis in the emergency department.Ultrasound J. 2019 Jun 11;11(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s13089-019-0128-5. Ultrasound J. 2019. PMID: 31359172 Free PMC article.
-
Classic yet challenging case of stump appendicitis: a case report.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024 Oct 24;86(12):7427-7430. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002694. eCollection 2024 Dec. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39649854 Free PMC article.
-
Stump appendicitis 5 years after laparoscopic appendicectomy.BMJ Case Rep. 2016 Oct 27;2016:bcr2016217022. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2016-217022. BMJ Case Rep. 2016. PMID: 27789546 Free PMC article.
-
An unusual case of perforated stump appendicitis: A case report.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022 Mar 9;76:103447. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103447. eCollection 2022 Apr. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35308435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bickell N.A., Aufses A.H., Jr., Rojas M., Bodian C. How time affects the risk of rupture in appendicitis. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2006;202(3):401–406. - PubMed
-
- Rose T. Recurrent appendiceal abscess. Med. J. Aust. 1945;32:659–662.
-
- Harris C.R. Appendiceal stump abscess ten years after appendectomy. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 1989;7(4):411–412. - PubMed
-
- Devereaux D.A., McDermott J.P., Caushaj P.F. Recurrent appendicitis following laparoscopic appendectomy Report of a case. Dis. Colon. Rectum. 1994;37(7):719–720. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials