Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3, Mediated Remodeling of the Tumor Microenvironment Results in Enhanced Tumor Drug Delivery in a Mouse Model of Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 26255562
- PMCID: PMC4863449
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.07.058
Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3, Mediated Remodeling of the Tumor Microenvironment Results in Enhanced Tumor Drug Delivery in a Mouse Model of Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
Background & aims: A hallmark of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is the presence of a dense desmoplastic reaction (stroma) that impedes drug delivery to the tumor. Attempts to deplete the tumor stroma have resulted in formation of more aggressive tumors. We have identified signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 3 as a biomarker of resistance to cytotoxic and molecularly targeted therapy in PDAC. The purpose of this study is to investigate the effects of targeting STAT3 on the PDAC stroma and on therapeutic resistance.
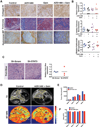
Methods: Activated STAT3 protein expression was determined in human pancreatic tissues and tumor cell lines. In vivo effects of AZD1480, a JAK/STAT3 inhibitor, gemcitabine or the combination were determined in Ptf1a(cre/+);LSL-Kras(G12D/+);Tgfbr2(flox/flox) (PKT) mice and in orthotopic tumor xenografts. Drug delivery was analyzed by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging mass spectrometry. Collagen second harmonic generation imaging quantified tumor collagen alignment and density.
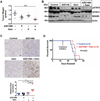
Results: STAT3 activation correlates with decreased survival and advanced tumor stage in patients with PDAC. STAT3 inhibition combined with gemcitabine significantly inhibits tumor growth in both an orthotopic and the PKT mouse model of PDAC. This combined therapy attenuates in vivo expression of SPARC, increases microvessel density, and enhances drug delivery to the tumor without depletion of stromal collagen or hyaluronan. Instead, the PDAC tumors demonstrate vascular normalization, remodeling of the tumor stroma, and down-regulation of cytidine deaminase.
Conclusions: Targeted inhibition of STAT3 combined with gemcitabine enhances in vivo drug delivery and therapeutic response in PDAC. These effects occur through tumor stromal remodeling and down-regulation of cytidine deaminase without depletion of tumor stromal content.
Keywords: Drug Delivery; Pancreatic Cancer; Stroma; Tumor Microenvironment.
Copyright © 2015 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Comment in
-
A New Scalpel for the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer: Targeting Stromal-Derived STAT3 Signaling.Gastroenterology. 2015 Dec;149(7):1685-8. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.10.028. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Gastroenterology. 2015. PMID: 26526714 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- Komar G, Kauhanen S, Liukko K, et al. Decreased blood flow with increased metabolic activity: a novel sign of pancreatic tumor aggressiveness. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:5511–5517. - PubMed
-
- Algül H, Treiber M, Lesina M, et al. Mechanisms of disease: chronic inflammation and cancer in the pancreas--a potential role for pancreatic stellate cells? Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;4:454–462. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

