Heterotypic Signals from Neural HSF-1 Separate Thermotolerance from Longevity
- PMID: 26257177
- PMCID: PMC4889220
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.07.026
Heterotypic Signals from Neural HSF-1 Separate Thermotolerance from Longevity
Abstract
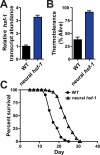
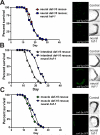
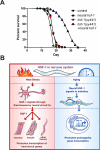
Integrating stress responses across tissues is essential for the survival of multicellular organisms. The metazoan nervous system can sense protein-misfolding stress arising in different subcellular compartments and initiate cytoprotective transcriptional responses in the periphery. Several subcellular compartments possess a homotypic signal whereby the respective compartment relies on a single signaling mechanism to convey information within the affected cell to the same stress-responsive pathway in peripheral tissues. In contrast, we find that the heat shock transcription factor, HSF-1, specifies its mode of transcellular protection via two distinct signaling pathways. Upon thermal stress, neural HSF-1 primes peripheral tissues through the thermosensory neural circuit to mount a heat shock response. Independent of this thermosensory circuit, neural HSF-1 activates the FOXO transcription factor, DAF-16, in the periphery and prolongs lifespan. Thus a single transcription factor can coordinate different stress response pathways to specify its mode of protection against changing environmental conditions.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R00 AG042495/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AG042495/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG042679/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P40 OD010440/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- 1K99AG042495/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES021667/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG000266/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37AG024365/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32AG000266/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG024365/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG025549/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01AG043080/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG043080/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01ES021667/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG042679/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG025549/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

